Folate receptor α (FOLR1 / FRα) is a high-affinity folate-binding protein and one of the major folate transporters. Overexpression of FOLR1 is often associated with accelerated cancer progression and poor patient prognosis . Common mammalian folate transporters include the reduced folate carrier (RFC); the proton-coupled folate transporter (PCFT); and folate receptors (FOLRs). Because FRα is overexpressed in a range of solid tumors, including ovarian, lung, and breast cancer, it is an attractive anticancer drug target.

(Data source: Nawaz FZ, et al. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2022)
Expression distribution of FOLR1
FOLR1 is mainly expressed in cytotrophoblasts, secretory cells, type 1 pneumocytes, syncytiotrophoblasts, type 2 pneumocytes, collecting duct cells, proximal tubule cells, mammary gland cells, and ciliated cells.

(Data source: Uniprot)
FRα shows restricted tissue expression in the kidney, lung, ovary, fallopian tube, uterus, cervix, aconite, and placenta and is highly expressed in approximately 80% of epithelial ovarian cancers ( EOC ).
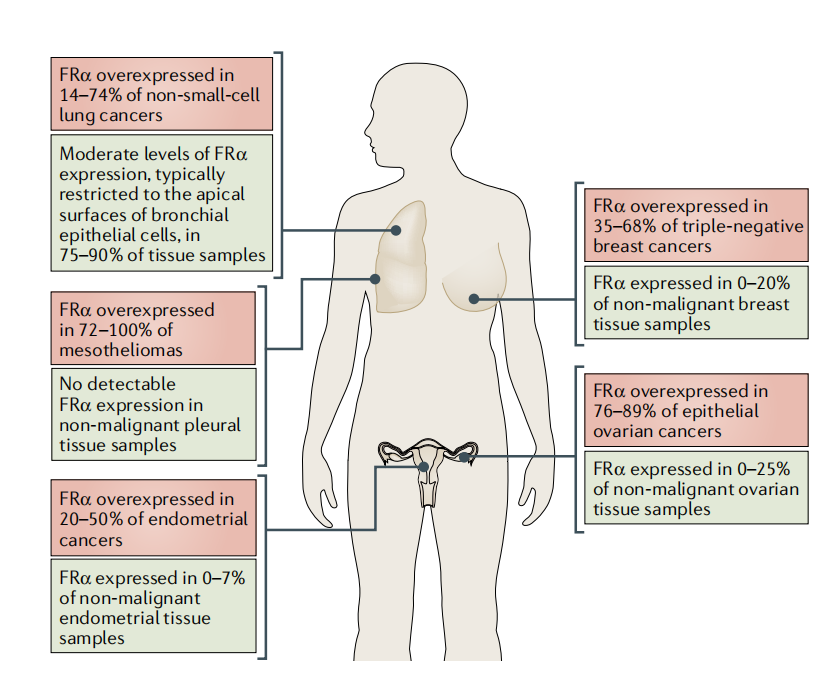
(Data source: Scaranti M, et al. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2020.)
FOLR1 signaling pathway and regulation
FOLR1 not only plays a role in folate metabolism but may also directly participate in cell signaling, affecting cell proliferation, migration, and survival. It plays a direct role in three signaling pathways: JAK-STAT3; ERK1/2; and as a transcription factor.
The role of FOLR1 in JAK-STAT3 signaling: Folic acid (FA) binds to FOLR1 and activates the JAK-STAT3 signaling pathway, likely through interaction with the gp130 co-receptor. Following FA stimulation, STAT3 becomes phosphorylated and dimers form, translocating to the nucleus to regulate gene expression.
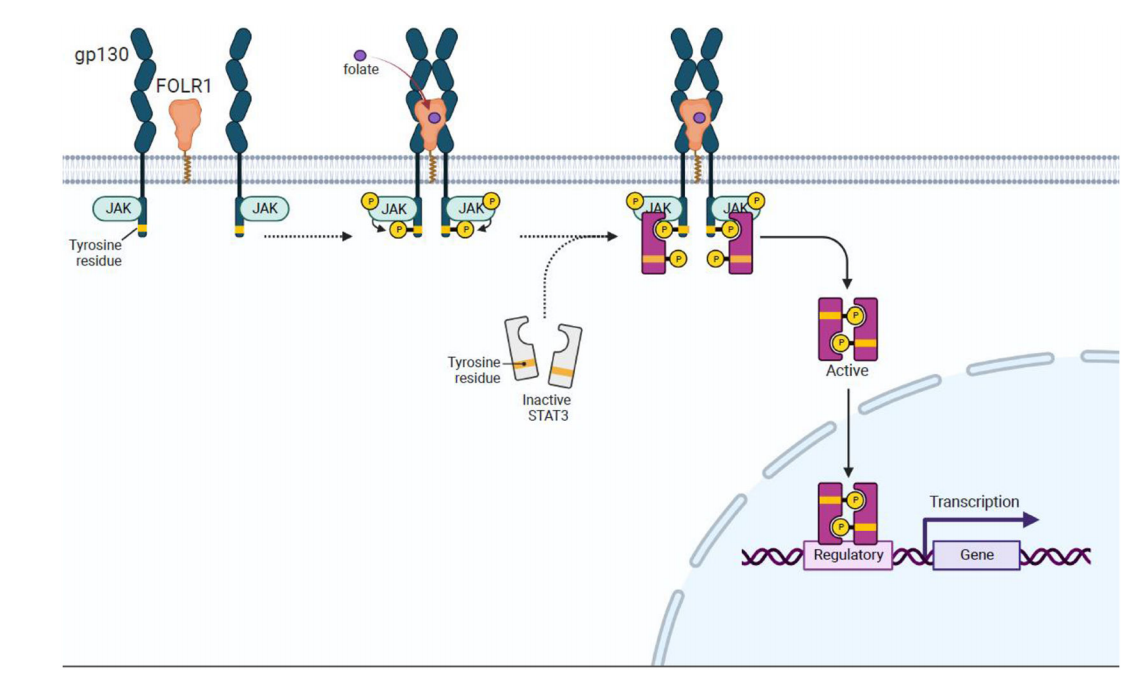
FOLR1 in ERK1/2 signaling: After binding to folic acid, FOLR1 may activate the ERK1/2 signaling pathway through interaction with SRC kinase and estrogen receptor (PGR). Activated ERK1/2 further affects downstream transcription factors such as NF-κB and p53.

FOLR1 acts as a transcription factor: Folate (FA) enters the cytoplasm through the action of RFC or membrane-localized FOLR1. Cytoplasmic FOLR1 binds FA and then translocates to the nucleus, where it acts as a transcription factor, directly binding to gene regulatory regions.
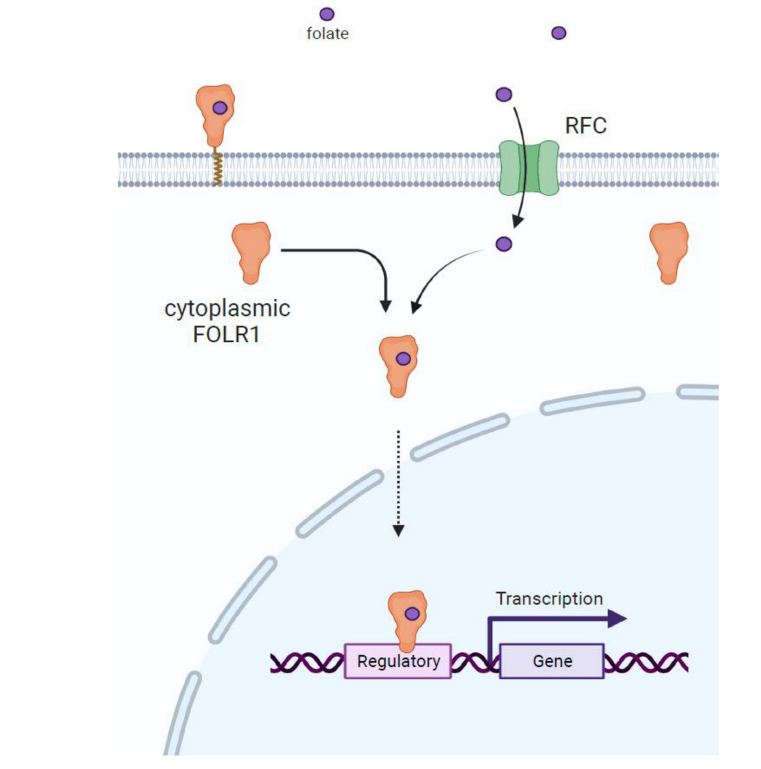
(Data source: Nawaz FZ, et al. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2022)
FOLR1 -targeted therapy
FRα is highly expressed in malignant tumors, making it a potential target for anti-tumor drug development. Multiple strategies have been explored, including monoclonal antibodies, antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), CAR T cells specifically targeting FRα, vaccines, small molecules, and folate-drug conjugates. Several clinical trials involving drugs targeting FRα are currently underway.

(Data source: Scaranti M, et al. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2020)
Farletuzumab (MORab003; Morphotek Ltd.) is the first anti-FRα monoclonal antibody with potential anti-tumor activity through the induction of antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC), and sustained tumor cell autophagy, leading to reduced cell proliferation and inhibition of the Lyn kinase signaling pathway. In a phase I study, farletuzumab demonstrated negligible toxicity in patients with ovarian cancer. In a phase II study, farletuzumab , in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel, improved response rates and duration of response in patients with platinum-sensitive ovarian cancer. Unfortunately, progression-free survival (PFS) was not achieved in a phase III clinical trial in patients with ovarian cancer. Despite this, farletuzumab was selected as the anti-FRα component of the ADC agent MORAb-202.
MORAb-202, an ADC that combines the humanized anti-human FRα antibody farletuzumab with the microtubule-targeting drug eribulin , has demonstrated significant anti-cancer efficacy in cancer cell lines and patient-derived xenograft models. In the United States, eribulin is a licensed drug for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer. MORAb-202 is currently in a Phase I/II clinical trial evaluating its efficacy in FRα -positive solid tumors.
Mirvetuximab soravtansine (MIRV) is the only FDA -approved antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) consisting of an FRα -binding antibody and the maytansinoid-like payload DM4, a microtubule inhibitor. MIRV is designed to target and kill FRα -positive cancer cells . It received accelerated FDA approval in 2022 for the treatment of patients with FRα-positive, platinum-resistant epithelial ovarian, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal cancer who have received one to three prior systemic therapies. MIRV, also commercially known as ELAHERE, is administered intravenously every three weeks at a dose of 6 mg/kg, adjusted for ideal body weight, until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity . Approval was based on data from the Phase 3 SORAYA trial (NCT04296890). Elahere received full approval in March 2024 based on early data from the MIRASOL trial.
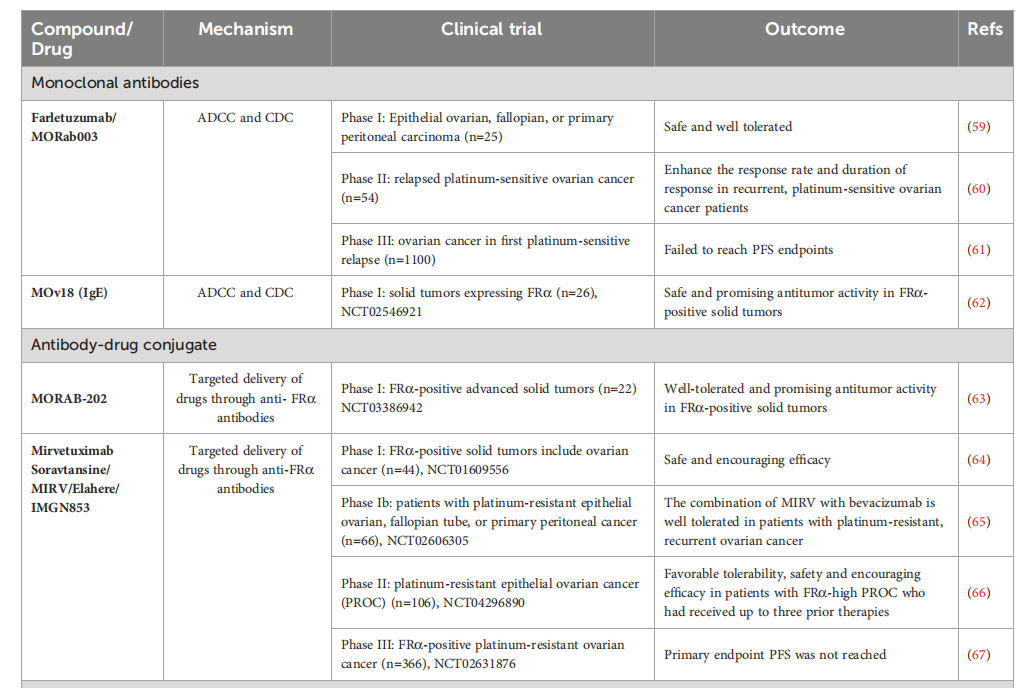

(Data source: Mai J, et al. Front Immunol. 2023)
