B7H3, also known as CD276, is a member of the B7 family of immune checkpoint proteins. This immune checkpoint molecule is selectively expressed by tumor cells and immune cells within the tumor microenvironment. High expression in cancer cells and activated tumor-infiltrating immune cells helps cancer cells evade surveillance by cytotoxic T cells and innate immune cells. In addition to its immune checkpoint function, B7H3 is also associated with tumor cell proliferation, metastasis, and treatment resistance. B7H3 has emerged as a promising therapeutic target for anti-cancer treatment.
B7H3 expression distribution
B7H3 is expressed in immune cells such as monocytes, dendritic cells, myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), neutrophils, macrophages, B cells, and activated T cells.
B7H3 is overexpressed in tumor tissues and expressed at lower levels in normal tissues. Among normal tissues, B7H3 is expressed most highly in prostate tissue but is barely detectable in muscle tissue.

(Data source: uniprot)
Structure and composition of B7H3
The B7H3 gene is located at 15q24.1 and consists of 12 exons encoding 316 amino acids. It is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein with two isoforms (2IgB7H3 and 4IgB7H3). The 2IgB7-H3 structure consists of a single extracellular V-like and C-like Ig domain, a transmembrane region, and a 45-amino acid cytoplasmic tail. The dominantly expressed form of human 4IgB7-H3 contains tandemly repeated VC domains and four Ig-like domains.

(Data source: Getu AA, et al. Mol Cancer. 2023)
Function of B7H3
B7H3's immune function: B7H3 was initially identified as promoting CD4+ T cell growth and inhibiting CD8+ T cell growth. Activated CD4+ T cells induce IFN-γ production and promote IL-12 production, while CD8+ T cells suppress IL-2, IL-10, IL-13, and IFN-γ production. B7H3 regulates the differentiation of tumor-associated macrophages, promoting the polarization of type 2 macrophages and shifting the M1 phenotype to the M2 phenotype.
Non-immunomodulatory functions of B7H3: B7H3 can also activate signaling pathways such as ERK, PI3K, and Stat3 in cancer cells, which may lead to accelerated cell proliferation and tumor growth.

(Data source: Zhao B, et al. J Hematol Oncol. 2022)
B7H3 and disease
B7H3 plays multiple roles in brain tumors, lung cancer, breast cancer, melanoma, liver cancer, gastric cancer, colorectal cancer, cervical cancer, and prostate cancer by activating different mechanisms. B7H3 is negatively correlated with the prognosis of glioma and ERG-negative prostate cancer and may serve as a promising immunotherapy target for brain tumors, lung cancer, and melanoma.

(Data source: Zhao B, et al. J Hematol Oncol. 2022)
B7H3 targeted therapy
Therapeutic strategies targeting B7H3 primarily include monoclonal antibodies, bispecific antibodies, antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), and CAR-T therapy. Many related antibody drugs are currently in clinical development.

(Data source: Getu AA, et al. Mol Cancer. 2023)
YL201 is an ADC developed by MediLink Therapeutics using its proprietary next-generation tumor microenvironment-activatable novel toxin linker platform technology (TMALIN®) conjugated to a highly specific B7-H3 antibody. It is intended for the treatment of nasopharyngeal carcinoma, small cell lung cancer, and metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. On October 8, 2024, MediLink Therapeutics and Amgen Inc entered into a global clinical research and drug supply collaboration agreement. Amgen will lead a global clinical study evaluating the potential of MediLink Therapeutics' B7-H3-targeting antibody-drug conjugate YL201 in combination with Amgen's bispecific T cell engager (BiTE®) targeting DLL3 and CD3, IMDELLTRA™, for the treatment of extensive-stage small cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC).
ifinatamab deruxtecan (I-DXd) , a potentially first-in-class B7-H3-directed antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) discovered by Daiichi Sankyo and jointly developed by Daiichi Sankyo and Merck, continues to demonstrate efficacy in previously treated patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC).
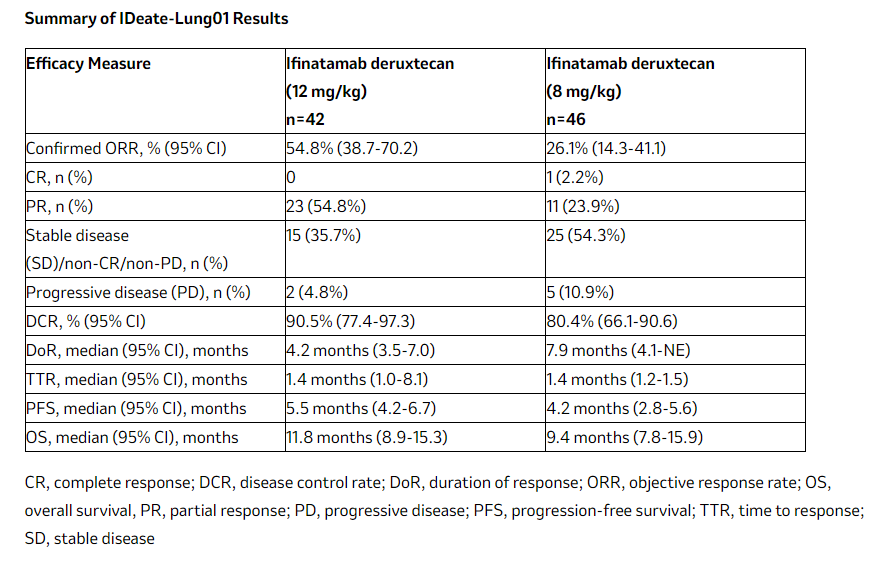
(Data source: Merck official website)
HS-20093 is a novel B7-H3-targeted ADC developed by Shanghai Hansoh Biological Technology Co., Ltd. It consists of a fully humanized B7-H3 monoclonal antibody covalently linked to a topoisomerase inhibitor (TOPOi) payload. It is being developed in multiple Phase I and Phase II clinical studies in China for the treatment of lung cancer, sarcomas, head and neck cancer, and other solid tumors. On September 9, 2024, Hansoh Pharmaceutical Group Co., Ltd. announced new progress in the ongoing ARTEMIS-001 trial. As of June 30, 2024, patients treated with HS-20093 at doses of 8.0 mg/kg and 10.0 mg/kg achieved an overall response rate (ORR) of 61.3% (n=31) and 50.0% (n=22), respectively, with a median progression-free duration of 5.9 months (n=31) and 7.3 months (n=22), respectively.
IBI-334 is a bispecific antibody targeting CD276 and EGFR developed by Innovent Biologics for the treatment of advanced cancers, advanced malignant solid tumors, and solid tumors. It is in Phase 1/2 clinical research.
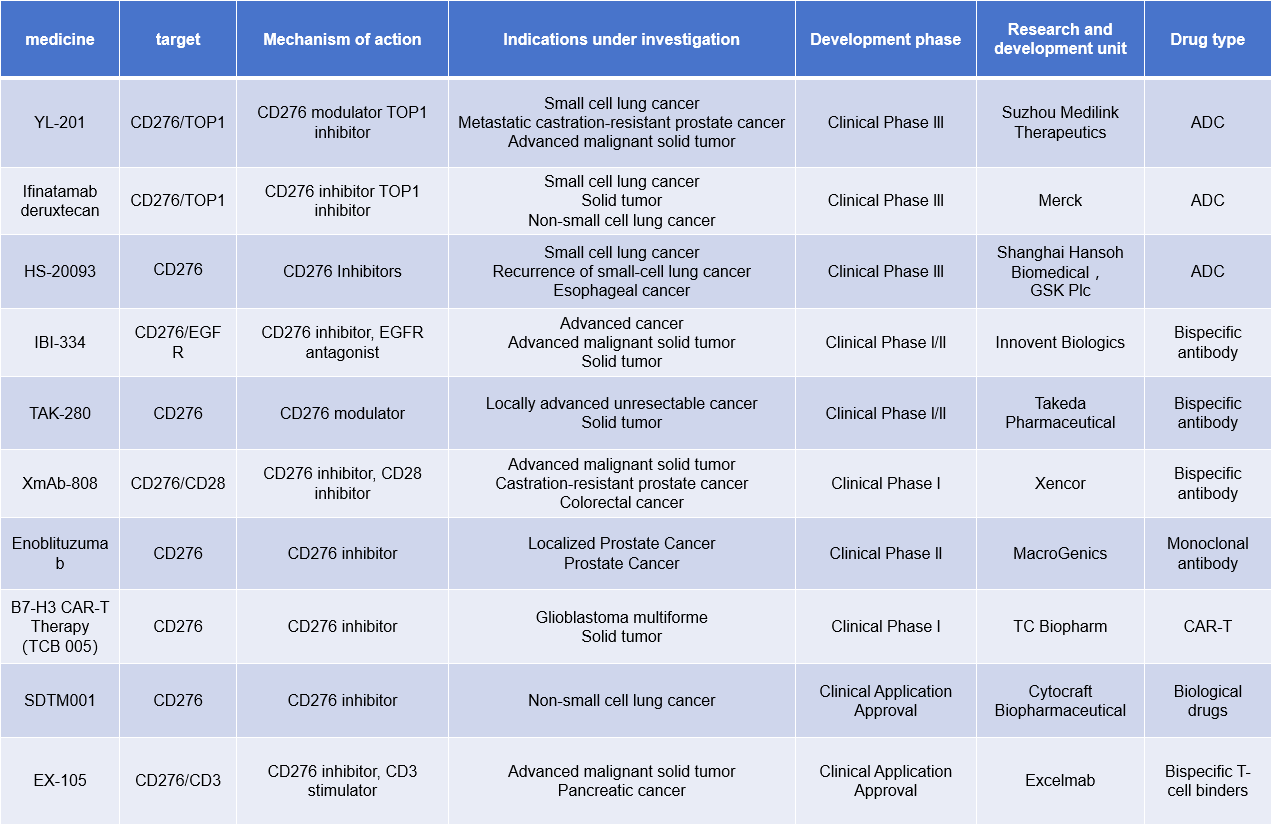
(Data source: New Drug Intelligence Database)
