CX3CL1 (also known as Fractalkine / Neurotactin), also known as chemokine (C-X3-C motif) ligand 1 , is the only member of the CX3C chemokine family. It has a unique structure and dual functions (chemotaxis and adhesion), mainly exerting its effects through its specific receptor CX3CR1 (G protein-coupled receptor). It plays different functions (chemotaxis and adhesion) according to its different configurations (soluble and membrane-bound).
a)Soluble CX3CL1: Produced by hydrolysis and release of the membrane-bound form by proteases (ADAM10/17), it has strong chemotactic activity for monocytes, T cells, and NK cells, mediating their migration to sites of inflammation or tumors. It synergistically enhances the recruitment of lymphocytes by other chemokines (such as MIP-1β and IL-8).
b)Membrane-bound CX3CL1: directly binds to CX3CR1 through its chemokine domain, mediating rapid and firm adhesion of leukocytes to endothelial cells at physiological flow rates, and is independent of integrins or glycosaminoglycans.
CX3CL1 expression distribution
CX3CL1 is primarily expressed (at the protein level) in seminal plasma, endometrial fluid, and follicular fluid. It is also expressed in the small intestine, colon, testes, prostate, heart, brain, lung, skeletal muscle, kidney, and pancreas. Its highest levels are in the brain and heart.
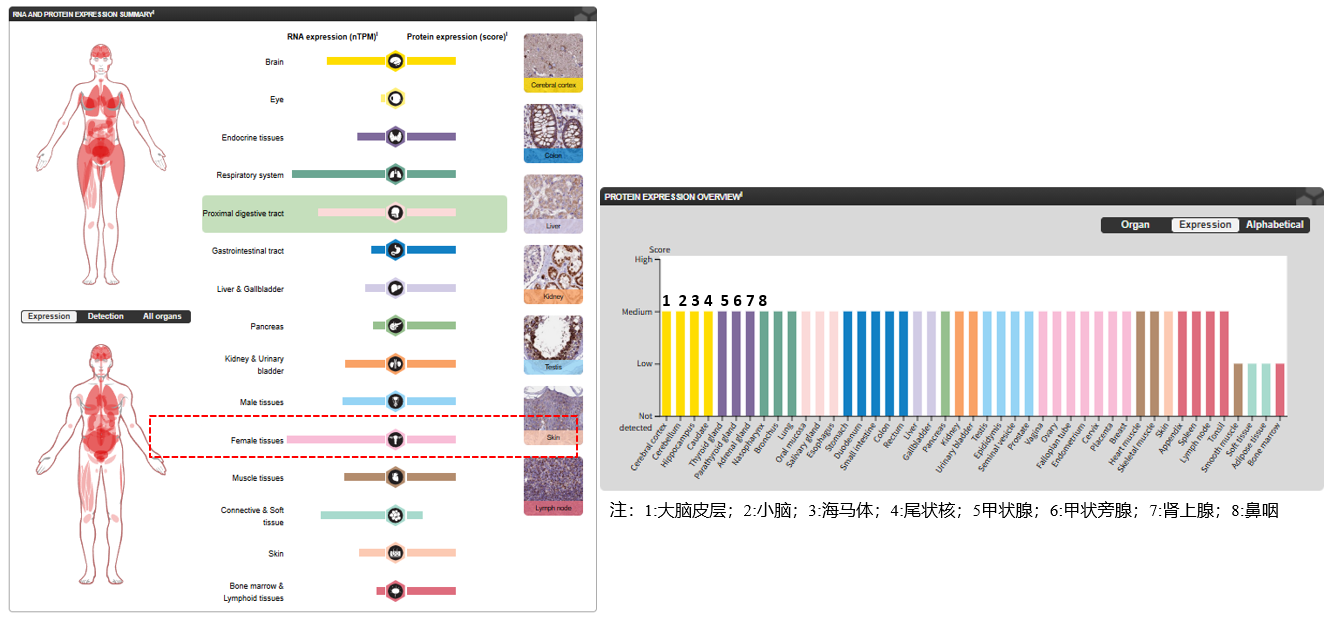
(Data source: uniprot)
Structure of CX3CL1
CX3CL1 is a type I transmembrane protein encoded by the CX3CL1 gene . It is 397 amino acids long and has a molecular weight of approximately 42.2 kDa. Its primary structure contains three amino acids between the first two cysteine residues. CX3CL1 can function as a membrane-bound protein or be released into a soluble form through protease cleavage. CX3CL1 exerts its effects by binding to its sole receptor, CX3CR1. Its structural features are as follows:
Chemokine domain: located at positions 1-76 of the N-terminus (containing the Cys¹⁻X³⁻Cys² motif) , it is mainly responsible for binding to the CX3CR1 receptor, mediating chemotaxis and adhesion; the unique three-amino acid interval distinguishes it from other chemokine families.
Mucin-like stem: This region is a highly glycosylated extended stem (approximately 250 AA) that is responsible for supporting the chemokine domain away from the cell membrane; the enhanced rigidity due to glycosylation facilitates receptor capture.
Transmembrane domain: hydrophobic α-helix , mediates the anchoring of the molecule to the membrane; forms dimers/polymers, enhances adhesion strength and prevents leukocyte rolling.
Cytoplasmic tail: The C-terminal 37 amino acids are responsible for connecting to the cytoskeleton (such as actin), stabilizing adhesion complexes and transmitting intracellular signals.
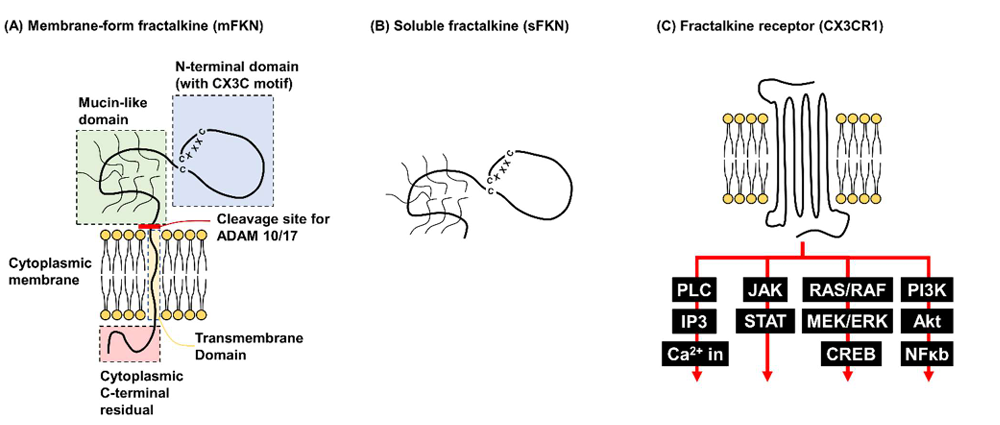
( Data source: Lee CY, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2025)
CX3CL1 signaling pathway
CX3CL1 (Fractalkine) mediates multiple signaling pathways through its sole receptor CX3CR1 (G protein-coupled receptor, GPCR), participating in immune regulation, tumor metastasis, neural regulation and other processes. Its signaling pathways are as follows:
Classical GPCR signaling pathways: CX3CR1 activation triggers a downstream cascade through G proteins (primarily Gαi): a) PLCβ-PKCα-c-Src pathway: CX3CL1 binds to CX3CR1, activating phospholipase Cβ (PLCβ), which hydrolyzes PIP₂ to IP₃ and DAG, leading to calcium release and activation of protein kinase Cα (PKCα), which in turn phosphorylates c-Src kinase. This pathway promotes cell migration and invasion (for example, through upregulation of ICAM-1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma) . b) cAMP inhibition: Gαi inhibits adenylate cyclase, reducing cAMP levels and affecting cell adhesion and chemotaxis.
PI3K/AKT-MAPK/ERK-HIF-1α pathway: In the hypoxic tumor microenvironment (such as prostate cancer and pancreatic cancer), CX3CL1/CX3CR1 activates the PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK pathways, promotes the expression of transcription factors NF-κB and HIF-1α, upregulates genes such as MMP-9 and GLUT-1, and enhances tumor cell metastasis and glycolysis.
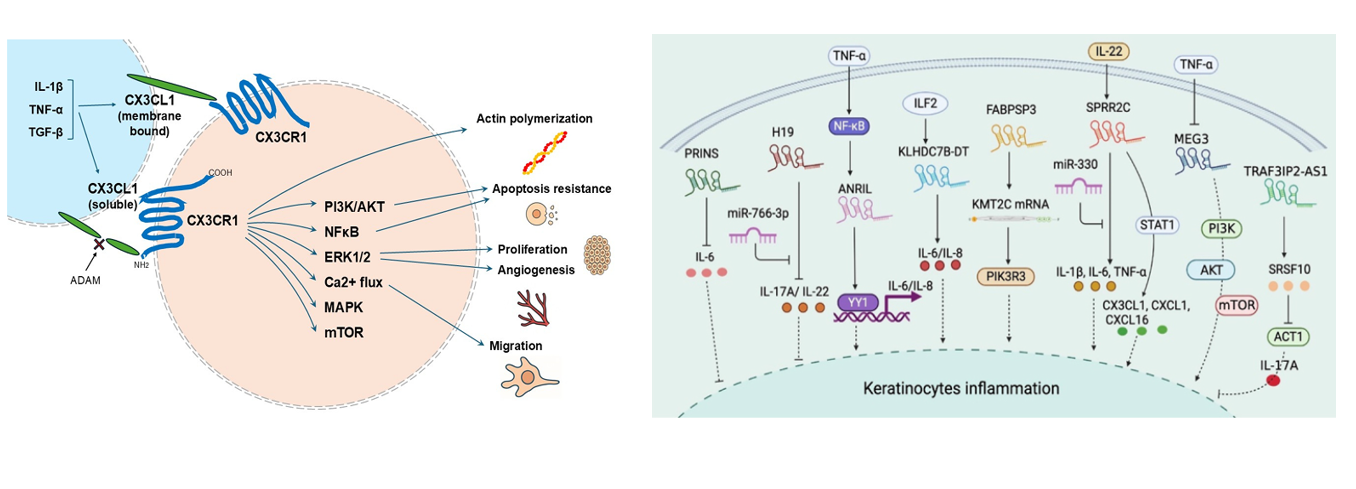
(Data source: Iwahashi Y, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2025, left; Shi R, et al. RNA Biol. 2023, right)
CX3CL1 and disease
Abnormal function of CX3CL1 (Fractalkine) is closely related to a variety of diseases, mainly due to imbalances in its immune regulation, inflammation mediation, and cell migration.
Diabetic Retinopathy (DR): In diabetic retinopathy, membrane-bound CX3CL1 (mFKN) released by damaged neurons is cleaved into a soluble form (sFKN). Activated microglia (which express CX3CR1) lose their vascular stabilization function, leading to leakage and exacerbated damage through the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines. Exogenous sFKN induces microglia to return to a quiescent state through CX3CR1, reducing inflammation and leakage, but its effect on angiogenesis is unclear.
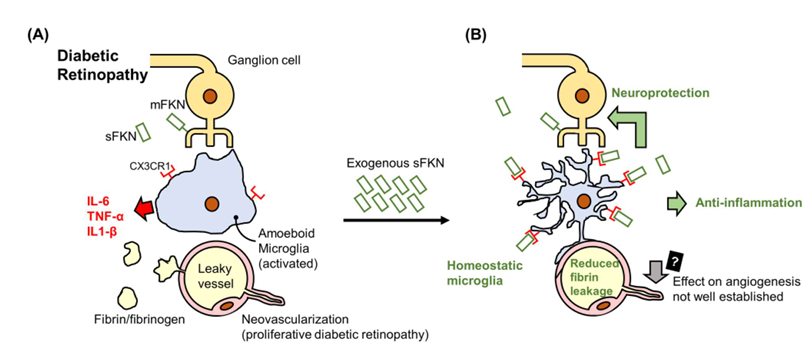
(Data source: Lee CY, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2025)
In the field of non-obstructive coronary artery disease (NO-CAD): the main causes of NO-CAD include coronary microvascular dysfunction (CMD), atherosclerotic changes in the coronary microcirculation, and inflammation. Increased production of FKN/CX3CL1 in the inflamed endothelium activates multiple intracellular signaling pathways through the receptor CX3CR1: a) Coronary microvascular dysfunction: FKN stimulates endothelial cells (ECs), inhibiting nitric oxide (NO) production and angiogenesis, inducing endothelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT); b) Proinflammatory FKN binds to CX3CR1, activating NF-κB through TAK1, PI3K/Akt, and NIK. It also upregulates inflammatory responses through HIF-1α during hypoxia; c) Pro-atherogenic: FKN acts as an adhesion molecule, recruiting monocytes expressing CX3CR1. Monocytes adhere to the endothelium, differentiate into macrophages, and internalize lipids to form foam cells, promoting atherosclerosis.
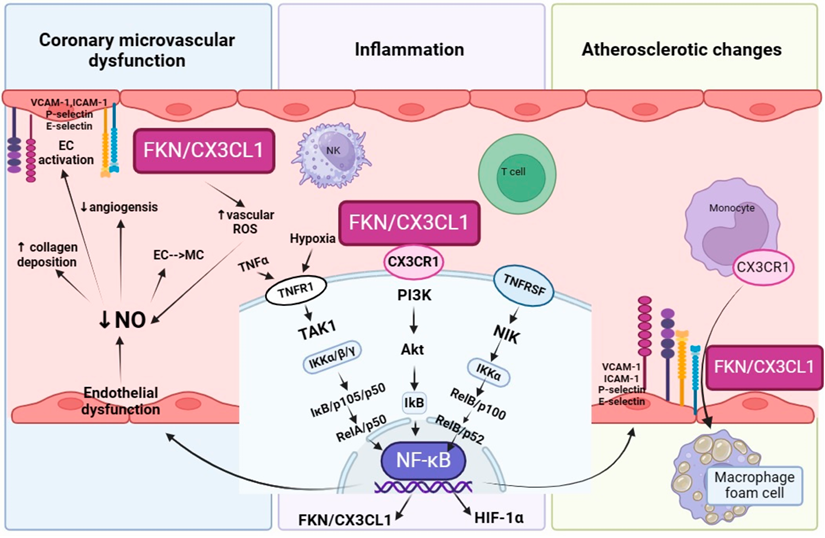
(Data source: Stangret A, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2024)
Osteoporosis: CX3CL1 overexpression → promotes osteoclast differentiation (regulated by NSUN5-mRNA methylation) → increased bone resorption.
Tumor metastasis: High expression of CX3CL1 → Recruitment of immunosuppressive cells (TAMs, MDSCs) expressing CX3CR1 → Formation of an immunosuppressive microenvironment, promoting the metastasis of pancreatic cancer and prostate cancer.
Targeted therapy for CX3CL1
Quetmolimab ( E6011 ) is a monoclonal antibody drug developed by Eisai Co., Ltd. that targets CX3CL1. Its primary mechanism of action is as a CX3CL1 antagonist, inhibiting its biological activity by blocking the binding of CX3CL1 to CX3CR1. It is used to treat Crohn's disease. It was approved for Phase 2 clinical trials in the United States on April 5, 2014.
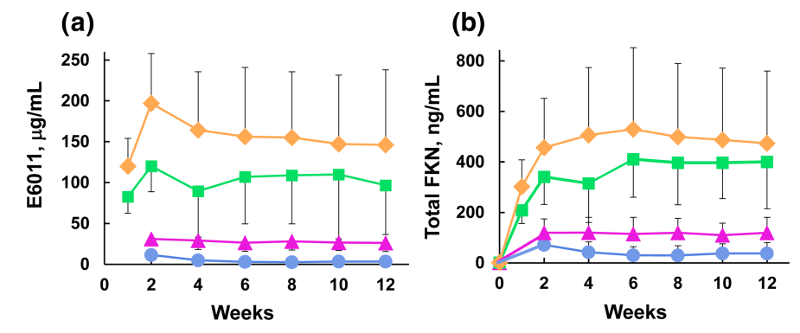
(Data source: Matsuoka K , et al. J Gastroenterol Hepatol . 2021)
CN117946265A is a monoclonal antibody targeting CX3CL1, developed by Hangzhou Bozhirui Biopharmaceutical Co., Ltd. It is primarily used to treat immune system disorders, cardiovascular diseases, and skin and musculoskeletal diseases. It is currently in the drug discovery phase.
WO2024050001A1 is a recombinant peptide drug targeting CX3CL1, developed by the University of Connecticut . It is primarily used to treat infections, neurological disorders, and endocrine and metabolic diseases. It is currently in the drug discovery phase.
