LILRB2 ( Leukocyte Immunoglobulin-Like Receptor B2 ) is an immune checkpoint molecule and a member of the LILR family. It is primarily expressed in myeloid cells (such as monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells) and certain tumor cells. 59 It binds to ligands (such as HLA-G, ANGPTLs, SEMA4A, and CD1d) to transmit inhibitory signals, suppressing the activity of immune cells and promoting tumor immune escape.
Expression distribution of LILRB2
Expressed in tolerogenic dendritic cells that contribute to the production of immunomodulatory IL-10. Expressed in myeloid-derived suppressor cells during pregnancy. Low levels of expression have been detected in natural killer (NK) cells. Also expressed in B cells.
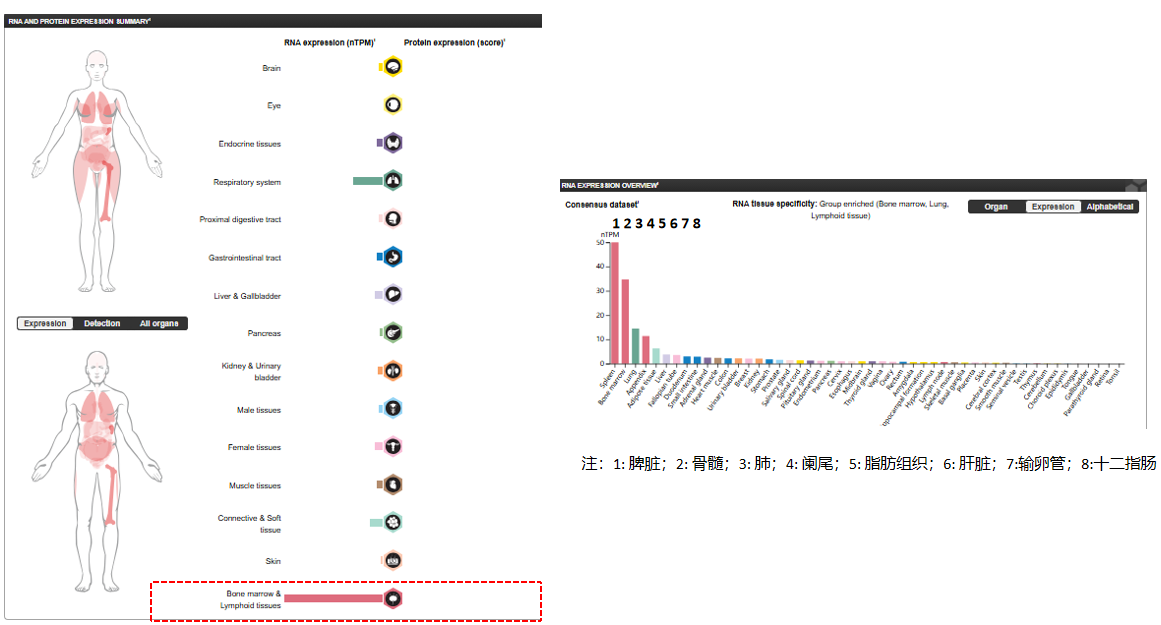
(Data source: Uniprot)
Function of LILRB2
a) Maintaining immune tolerance and homeostasis: It recognizes MHC class I molecules ("self" signals) on the surface of normal cells and transmits inhibitory signals to prevent overactivation of macrophages and dendritic cells or their attack on self-tissues. b) Inhibiting inflammatory responses: In the context of infection or inflammation, ligand binding to LILRB2 inhibits myeloid cell activation, cytokine production (such as TNF-α and IL-12), and the expression of co-stimulatory molecules, thereby negatively regulating the inflammatory response and preventing tissue damage. c) Promoting tumor immune evasion: Tumor cells often highly express MHC class I molecules (including HLA-G). These molecules bind to LILRB2 on tumor-infiltrating myeloid cells (such as tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs). d) Regulating antigen-presenting cell function: It inhibits the maturation and activation of dendritic cells, reducing their ability to stimulate T cells and promoting immune tolerance.
Structure of LILRB2
LILRB2 is a type I transmembrane protein encoded by the LILRB2 gene with a length of 597 AA and a molecular weight of approximately 65 kDa . It contains extracellular, transmembrane and intracellular domains . It is a key inhibitory immune receptor. Its structural characteristics are that the four extracellular Ig-like domains bind to MHC-I ligands and the intracellular ITIM motif relies on the recruitment of SHP-1/SHP-2 phosphatases.
Extracellular region (22-460 aa) : Contains four Ig-like C2-type 1 domains (D1, D2, D3, and D4) . The D1 and D2 domains are primarily responsible for ligand binding. They primarily recognize and bind to classical MHC class I molecules (such as HLA-A, -B, and -C) and non-classical MHC class I molecules (such as HLA-G). This binding is the basis for LILRB2's immunosuppressive function.
Transmembrane region (461-481 aa) : contains a positively charged amino acid residue ( Lys residue ), which forms a complex with the negatively charged adaptor protein DAP12 (DNAX-activating protein of 12 kDa); LILRB2 itself has no intrinsic signaling motif and requires DAP12 to transmit signals.
The C-terminal intracellular domain (482-597 aa) contains multiple serine/threonine phosphorylation sites, potentially involved in interactions with other signaling or scaffolding proteins. It also contains two or four (depending on the splice variant) immunoreceptor tyrosine inhibitory motifs. The ITIM is its core functional domain. Upon binding to ligands such as MHC-I, tyrosine residues in the ITIM are phosphorylated by Src family kinases. Phosphorylated ITIMs recruit and activate SH2 domain-containing tyrosine phosphatases, primarily SHP-1 and SHP-2.
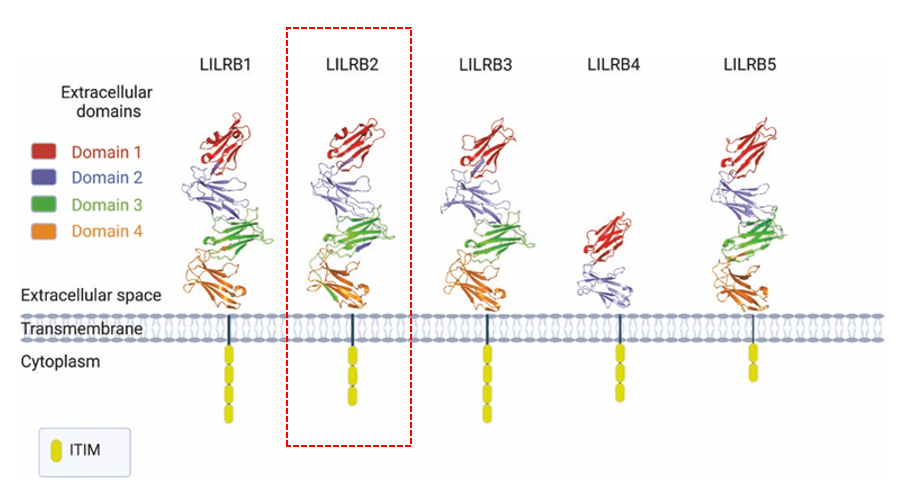
(Data source : Gomes R , et al. Immunother Adv. 2025)
Signaling pathway of LILRB2
The ITIM-SHP phosphatase pathway: a) Ligand binding : When LILRB2 binds to a ligand (such as MHC-I and HLA-G), tyrosine residues within the ITIM motif are phosphorylated by Src family kinases. b) Phosphatase recruitment : Phosphorylated ITIMs recruit the SH2 domain-containing tyrosine phosphatases SHP-1 (PTPN6) and SHP-2 (PTPN11). c) Downstream signaling inhibition : SHP-1/2 dephosphorylate and inhibit activated signaling pathways (such as Syk, PI3K/AKT, and MAPK pathways), blocking the activation of immune cells (such as macrophages and dendritic cells), phagocytosis, and the release of inflammatory factors. In platelets, SHP-1/2 inhibits collagen receptor GPVI and integrin αIIbβ3 signaling, reducing phosphorylation of LAT, SLP76, and PLCγ2, thereby inhibiting thrombosis.
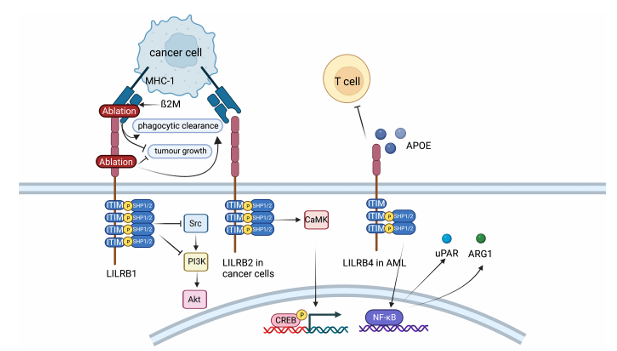
( Data source : Qian Y , et al. Chin J Cancer Res. 2022)
LILRB2 and disease
Hepatic fibrosis : ANGPTL8 secreted by hepatocytes under a high-fat diet binds to LILRB2 on the surface of hepatic stellate cells to activate ERK1/2 signaling, and through TGFβ1 positive feedback and autophagy regulation, promotes the expression of fibrosis genes such as α-SMA and CollagenⅠ to induce liver fibrosis. Metformin can inhibit ANGPTL8 and block this process.

(Data source : Zhang Z, et al. J Adv Res. 2023)
Lung cancer : Radiotherapy-induced activation of the cGAS-STING pathway leads to upregulation of LILRB2 expression in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), further promoting p16-dependent cellular senescence and the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP). This cascade ultimately activates the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway in NSCLC, driving tumor progression and enhancing radioresistance. From a therapeutic perspective, combining LILRB2 blockade with radiotherapy has the potential to enhance anti-tumor efficacy and prolong patient survival.
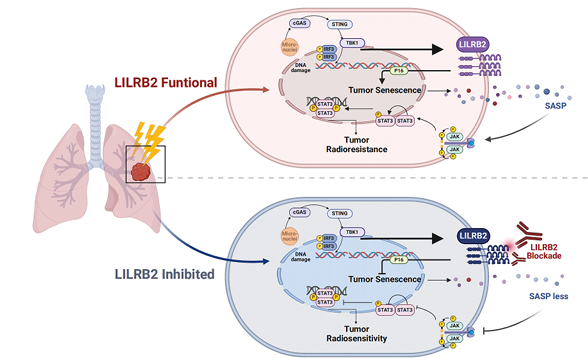
(Data source : Chen X, et al. Cancer Lett. 2024)
Breast cancer : LILRB2 is upregulated in breast cancer tissues and cells and is positively correlated with poor prognosis. This receptor promotes breast cancer progression by downregulating HLA-A expression. Its mechanism of action is as follows: LILRB2 promotes the interaction between the ubiquitin ligase membrane-associated RING finger protein 9 (MARCH9) and HLA-A, thereby mediating the ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of HLA-A. In a syngeneic transplant mouse model, breast cancer cells expressing LILRB2 successfully evaded CD8+ T cell cytotoxicity and suppressed cytokine secretion by cytotoxic CD8+ T cells.
Alzheimer's disease (AD): LILRB2 (human) or its mouse homolog PirB is a high-affinity receptor for β-amyloid (Aβ) oligomers. Binding activates downstream signaling, leading to enhanced cofilin signaling, disrupting the neuronal actin cytoskeleton, impairing synaptic plasticity and dendritic spine structure, and ultimately causing cognitive impairment and memory loss.
LILRB2 -targeted therapy
MK-4830 is a monoclonal antibody drug targeting LILRB2 , developed by Agenus, Inc. Its primary mechanism of action is as a LILRB2 inhibitor for the treatment of ovarian cancer and advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma . It was approved for Phase 2 clinical trials on June 26 , 2020 .
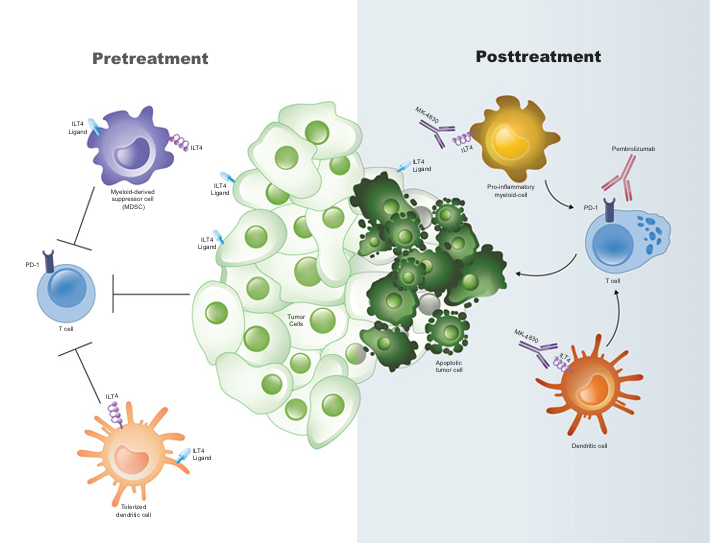
(Data source: Siu LL , et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2022)
OR502 , developed by OncoResponse, Inc., is a monoclonal antibody targeting LILRB2 . Its primary mechanism of action is as a LILRB2 regulator , intended for the treatment of advanced malignant solid tumors and cutaneous melanoma . It was approved for Phase 2 clinical trials on October 24 , 2023 .
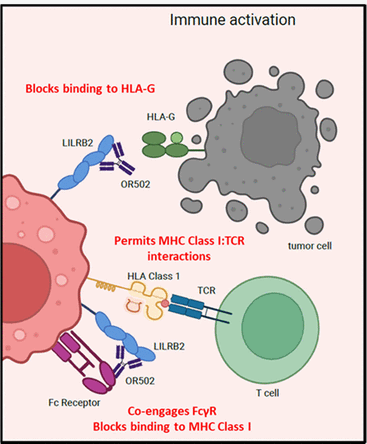
(Data source: Shiraj Sen , et al. Clinical Trial Completed. 2024)
IO-108 is a monoclonal antibody targeting LILRB2 developed by Immune-Onc Therapeutics . Its primary mechanism of action is as a LILRB2 inhibitor for the treatment of solid tumors . It was approved for Phase 1 clinical trials on September 30 , 2021 .
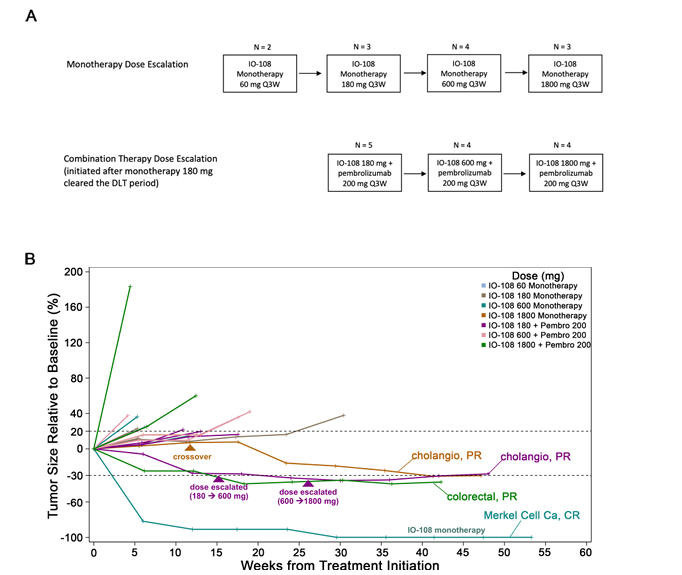
(Data source: Shiraj Sen , et al. Clinical Trial Completed. 2024)
Anti-LILRB2 nanobody (CN114805568A) is a nanobody drug targeting LILRB2 , developed by Beijing Kono Xincheng Technology Co., Ltd. Its primary mechanism of action is as a LILRB2 inhibitor for the treatment of solid tumors . It is currently in the preclinical stage.
