Human MAdCAM1 (Mucosal Addressin Cell Adhesion Molecule-1) is a cell adhesion molecule primarily expressed in the vascular endothelium of mucosal tissue. It binds to α4β7 integrins on the surface of immune cells, thereby promoting the targeted migration of immune cells (such as lymphocytes) to the intestinal mucosa and mediating inflammatory responses. Research on MAdCAM1 targets is of great significance in the fields of immunology and inflammatory bowel disease.
Expression distribution of MADCAM1
MADCAM1 is highly expressed in high endothelial venules (HEV) and venules of the small intestinal lamina propria, with lower expression in the colon and spleen. Very low levels of expression have been detected in pancreas and brain tissues, but not in thymus, prostate, ovary, testis, heart, placenta, lung, liver, skeletal muscle, kidney, or peripheral blood leukocytes.
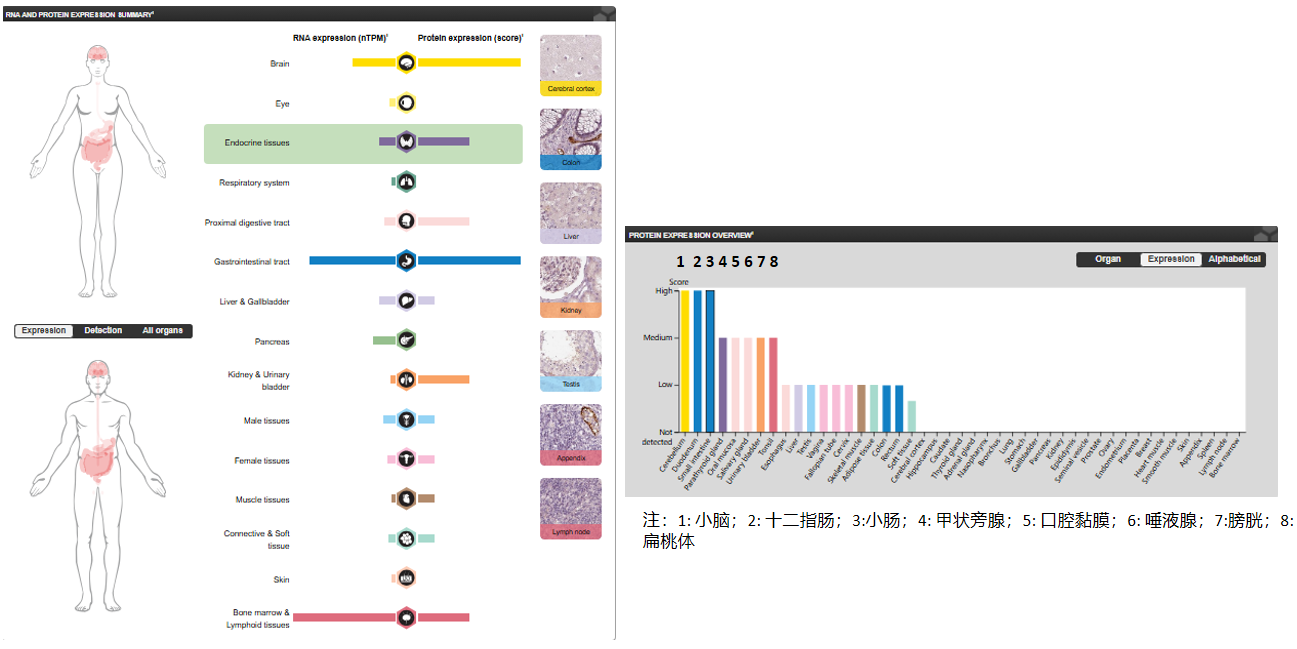
(Data source: Uniprot)
Structure of MADCAM1
MADCAM1 is encoded by the MADCAM1 gene, which is 382 aa, a type I transmembrane protein with a molecular weight of approximately 40.1 kDa, belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily (IgSF), contains extracellular, transmembrane and intracellular domains, and plays an important role in driving lymphocyte homing to mucosal tissues.
Extracellular region (19-317 aa) : The extracellular region contains two Ig-like domains and one Mucin -like domain. a) Two N-terminal Ig domains (IgD1-IgD2): D1 is of the IgV type, and D2 is of the IgC2 type. They specifically bind to integrin α4β7 and mediate stable lymphocyte adhesion to endothelial cells. b) Mucin-like domain: Adjacent to the D2 domain, it is heavily glycosylated and negatively charged. It binds L-selectin (CD62L) and initiates lymphocyte rolling on the endothelium. c) Membrane-proximal IgA homology domain (IgD3): Shares homology with immunoglobulin A, but its function is still unclear.
Transmembrane region (318-338 aa) : single transmembrane α-helix, anchored to the cell membrane.
Intracellular region (339-382 aa) : located in the cytoplasm , involved in membrane localization regulation.
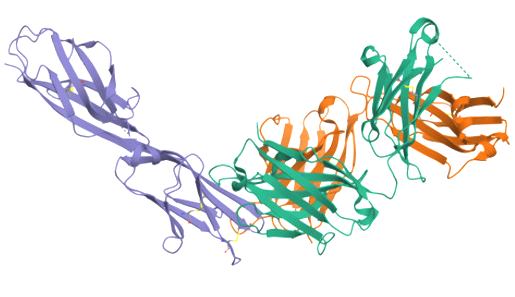
(Data source: PDB: 4HCR)
MADCAM1 signaling pathway
MAdCAM1 is regulated by the intestinal flora through the α4β7-MAdCAM1 axis, and plays a key role in cancer immune surveillance and immunotherapy (in mice and humans). The integrity of the axis affects the control effect of immunotherapy on tumors.
Eubiosis: Intestinal bacteria (such as Enterococci) maintain normal MAdCAM1 expression in the intestinal mucosa (mLNs, lamina propria). Within mesenteric lymph nodes (mLNs), mLN-primed IL-17 + RORγt + α4β7 + regulatory T cells (Tregs) utilize the α4β7-MAdCAM1 axis on high endothelial veins (HEVs) to expel immunosuppressive α4β7 + Tregs from the intestinal mucosa and migrate to tumors and tumor-draining lymph nodes (tdLNs), participating in immune regulation.
Dysbiosis: Antibiotic use disrupts the intestinal flora, inducing downregulation of MAdCAM 1 expression in the intestinal mucosa and mLNs. For example, a decrease in Enterococci disrupts the α4β7-MAdCAM 1 axis, impairing immune surveillance and weakening the effectiveness of immunotherapy.
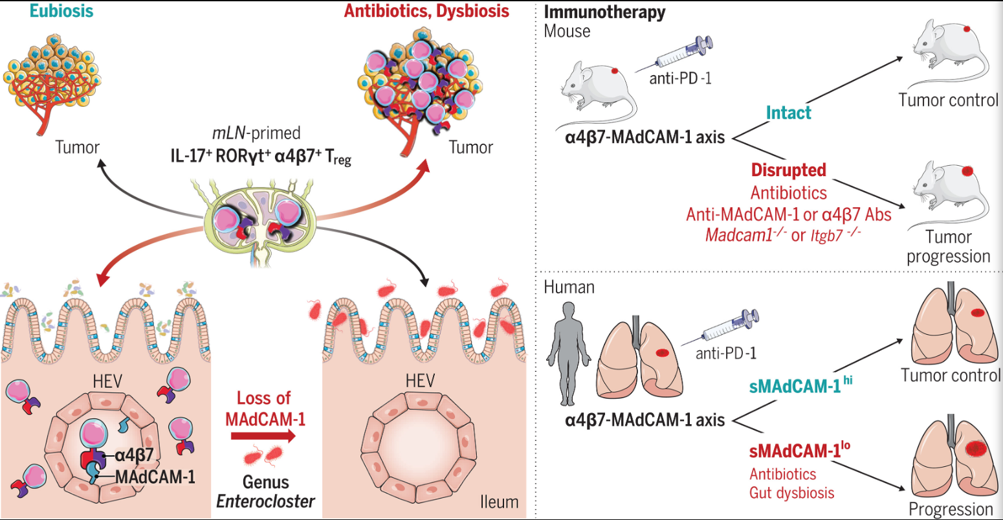
(Data source: Fidelle M , et al. Science. 2023)
MADCAM1 and disease
The MAdCAM-1/α4β7 pathway is the core hub for immune cell homing to the intestine. It integrates mechanical stimulation, chemotactic signals and phosphorylation networks, regulates inflammation and cancer progression, and is an important target for the treatment of autoimmune diseases.
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): Ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn's disease (CD) : Intestinal endothelial cells in the inflamed area highly express MAdCAM-1, promoting the infiltration of α4β7⁺ lymphocytes and exacerbating intestinal inflammation. Targeted blockade of MAdCAM-1 can reduce immune cell migration and has become a core therapeutic strategy for IBD. MAdCAM-1-mediated immune cell infiltration activates the IL-6/p-STAT3 and TNF-α/NF-κB pathways, driving chronic inflammation.

(Data source : He R , et al. Front Immunol . 2023)
Colitis-associated cancer (Colitic Cancer) : Chronic inflammation associated with IBD can induce colon cancer. MAdCAM-1 is highly expressed in cancerous tissues, promoting the infiltration of immune cells such as CD8 + and CD68 + , accelerating tumor progression. Anti-MAdCAM-1 antibodies can inhibit tumorigenesis and block inflammatory signaling pathways.
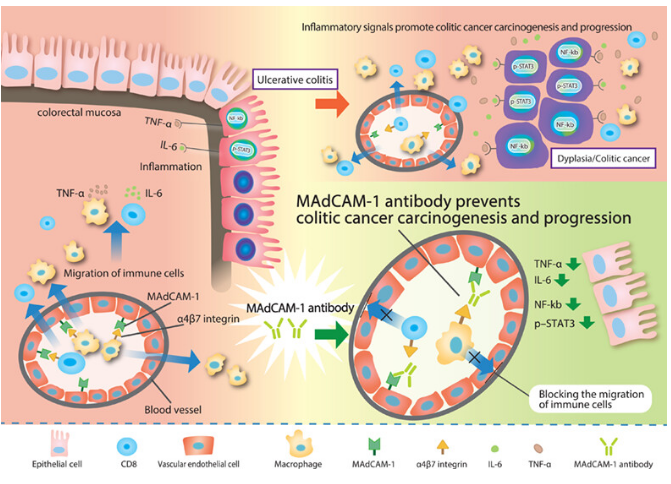
(Data source : Ozawa N , et al. Int J Cancer. 2024)
Targeted therapy for MADCAM1
PF-00547659 ( vedolizumab ) is a monoclonal antibody drug developed by Pfizer that targets MADCAM1. Its primary mechanism of action is as a MADCAM1 inhibitor, used to treat ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn's disease (CD). Vedolizumab is a fully humanized monoclonal antibody that blocks α4β7/MAdCAM-1 binding, acting directly in the intestine with a highly selective mechanism of action. A Phase II study demonstrated efficacy in patients with UC, but failed to demonstrate superiority over placebo in patients with CD. The drug was initially approved for Phase III clinical trials on December 5, 2017, but has since been terminated.

(Data source: Sandborn WJ , et al. Gastroenterology . 2020)
Ontamalimab (SHP-647), developed by Takeda, is a monoclonal antibody targeting MADCAM1 and CD3 . Its primary mechanism of action is as a MADCAM1 inhibitor, and it is currently in the finalization phase of Phase 3 clinical trials for the treatment of ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease.
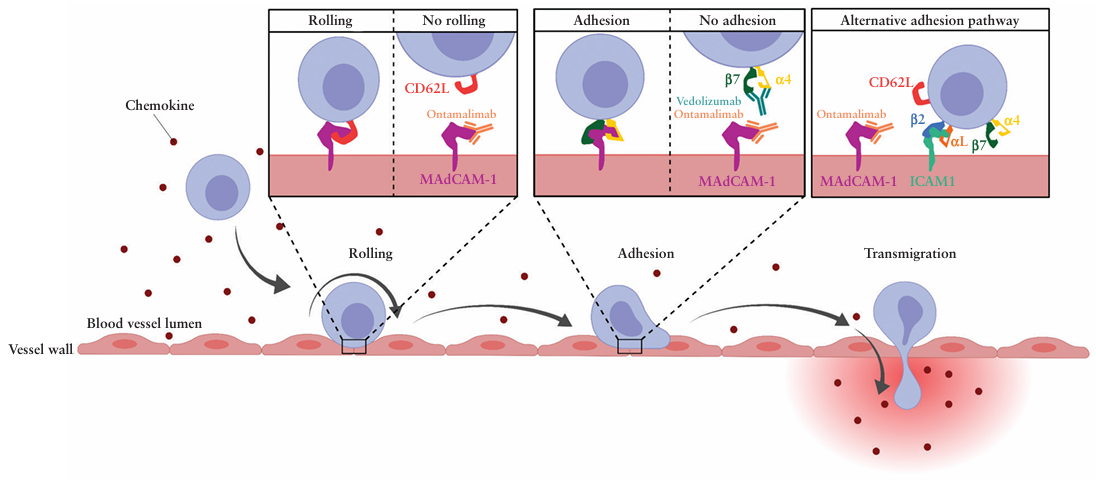
(Data source: Schulze LL , et al. J Crohns Colitis. 2023)
PT-002, developed by Pandion Therapeutics, is a monoclonal antibody targeting MADCAM1 and IL-2R. Its primary mechanism of action is as a MADCAM1 modulator and IL-2R agonist for the treatment of autoimmune diseases. It is currently in the preclinical stage.
