The Microtubule - Associated Protein Tau ( MAPT) gene, primarily functions in neurons to stabilize microtubules and promote their assembly . Under pathological conditions, Tau becomes hyperphosphorylated, causing it to dissociate from microtubules and form insoluble aggregates within cells. These aggregates are believed to be closely linked to the pathogenesis of various neurodegenerative diseases .
Expression distribution of MAPT
MAPT primarily expressed in neurons. The PNS-tau isoform is expressed in the peripheral nervous system, while the other isoforms are expressed in the central nervous system.
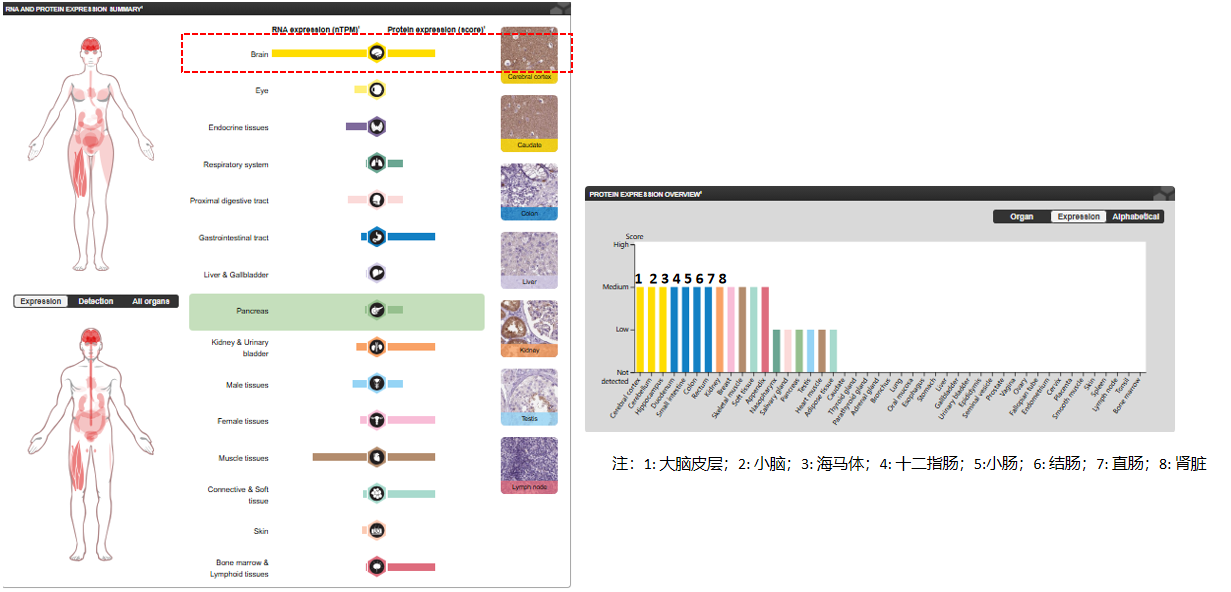
(Data source: Uniprot)
The structure of MAPT
MAPT , encoded by the MAPT gene, is a neuronal microtubule protein with a length of 758 amino acids and a molecular weight of approximately 78.9 kDa . MAPT produces six tau isoforms through alternative splicing, which dominate microtubule stability and axonal transport in neurons. The MTBR domain determines microtubule binding ability, while the N-terminus and phosphorylation sites regulate interactions and pathological aggregation. Its domain structure can be divided into the following parts:
N-terminal projection domain : located in the amino acid 1-150 aa region, responsible for interacting with cytoskeletal proteins and participating in signal transduction;
Proline-rich region: adjacent to the microtubule binding domain , responsible for regulating the phosphorylation sites of protein kinases (such as GSK-3β and CDK5);
Microtubule-binding domain (MTBR): located at the C-terminus (containing 3-4 repeat sequences: R1-R4), responsible for binding to microtubules; exon 10 splicing determines the 3R/4R type, and the 4R subtype has stronger binding ability.
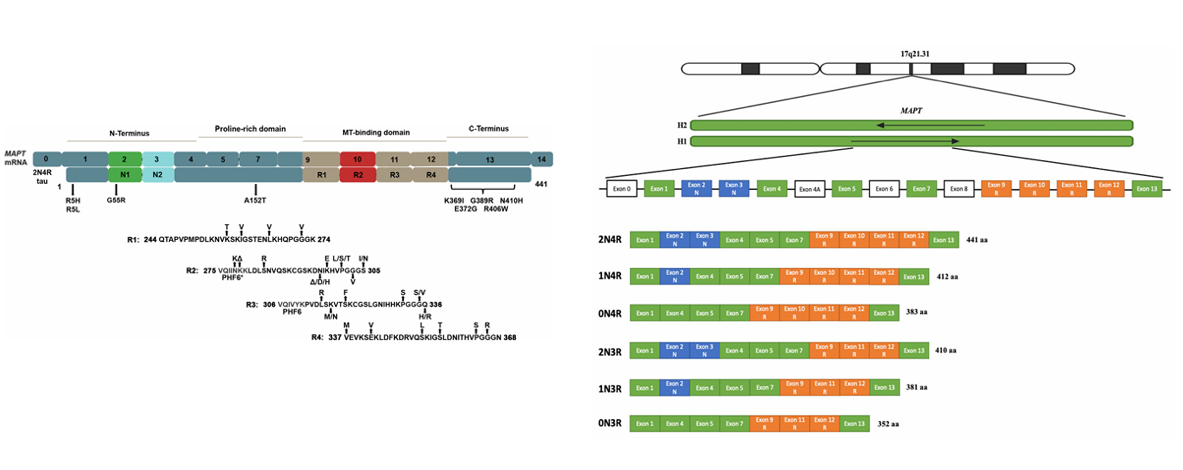
(Data sources : Strang KH , et al. Lab Invest. 2019 ; Leveille E , et al. Parkinsonism Relat Disord . 2021 )
Signaling pathway of MAPT
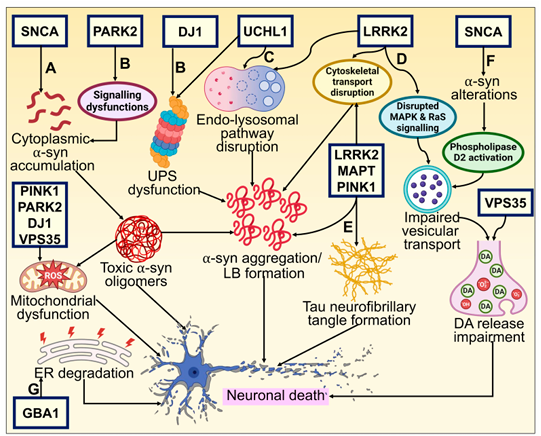
Tau aggregation inhibits autophagy: Abnormal tau protein aggregation (such as hyperphosphorylation or truncation) inhibits the expression of the IST1 gene through the CEBPB-ANP32A-INHAT pathway, leading to decreased IST1 protein levels. IST1 is a positive regulator of the endosomal sorting complex ESCRT-III. Its loss hinders the formation of the ESCRT-III complex (including components such as CHMP2B and CHMP4B), thereby inhibiting the fusion of autophagosomes and lysosomes and causing autophagy disorders.
Pathological phosphorylation : Overactivation of kinases (GSK-3β, CDK5) or inactivation of phosphatases (PP1, PP2A) leads to abnormal phosphorylation of Tau (such as P-tau-S396), detachment from microtubules and aggregation, inducing synaptic dysfunction and neuronal death.
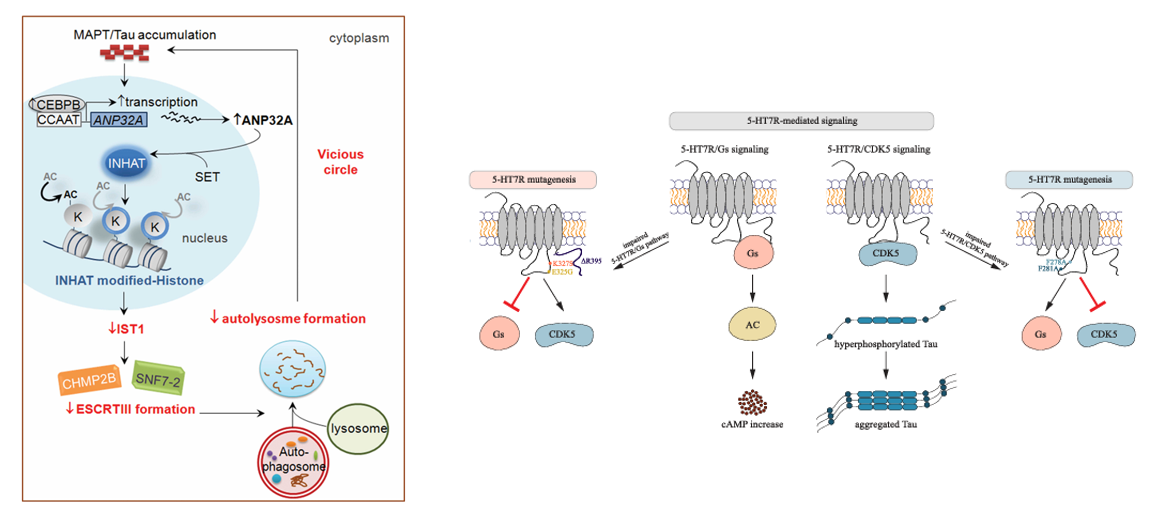
( Data source : Feng Q, et al. Autophagy. 2020; Ackmann J, et al. Cell Commun Signal. 2024)
MAPT and disease
MAPT (microtubule-associated tau protein) gene mutation or dysfunction is the core pathological mechanism of many neurodegenerative diseases, which mainly leads to abnormal aggregation of tau protein to form neuronal inclusion bodies, causing neuronal dysfunction and death.
Alzheimer's disease AD ) : In Alzheimer's disease, extracellular senile plaques composed of amyloid-β and aggregated tau are present. These abnormal proteins interact with surface receptors, activating the pathological Rho-GTPase signaling pathway. Amyloid-β exposure hyperactivates Rho-GTPases (e.g., phosphorylation at Y42). This overactivation in turn enhances ROCK kinase activity. ROCK phosphorylates and activates Src (at Y416), which in turn activates GSK-3β, promoting tau hyperphosphorylation. It also inhibits HDAC6 activity (which promotes tau and tubulin acetylation). These post-translational modifications of tau ultimately lead to its aggregation.

(Data source : Desale SE, et al. Mol Biomed. 2021)
Familial Alzheimer 's Disease ( FAD ) : FAD - related PS1 mutations increase the activity of γ-secretase, activate kinases ( such as GSK3) through APP-βCTF, and cause Tau hyperphosphorylation and aggregation; cells synchronously upregulate heat shock proteins (HSP90/70) and enhance autophagy (with the participation of LC3-II and Lamp2) in an attempt to clear abnormal proteins, but under long-term pathological pressure, the protective mechanism may fail, ultimately promoting the progression of AD pathology.
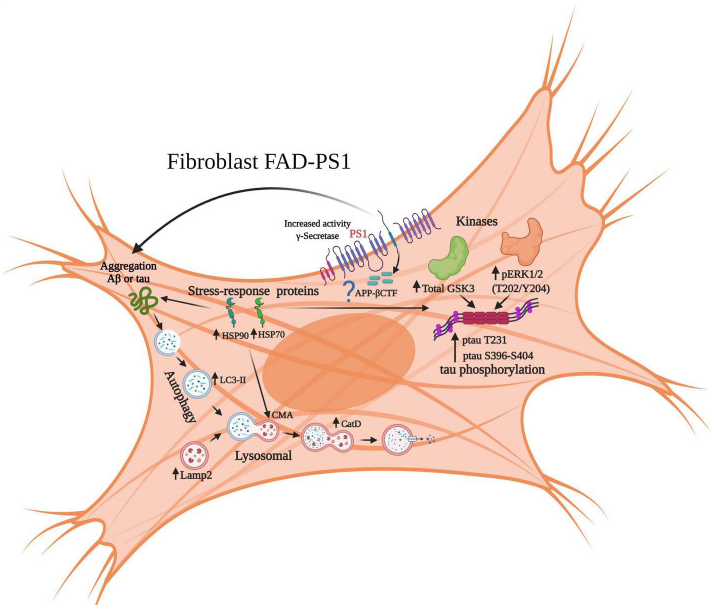
(Data source : Lopez-Toledo G, et al. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022)
Parkinson's Disease (PD) : Tau is hyperphosphorylated in certain brain regions (such as the substantia nigra and striatum) in PD patients, causing it to detach from microtubules, misfold, and aggregate into neurofibrillary tangles. This aggregation directly disrupts microtubule structure, blocking signaling and transport within neurons. Tau can also synergize with pathological events such as α-synuclein to accelerate the death of dopaminergic neurons.
(Data source : Ratan Y , et al. Biomolecules. 2024)
Targeted therapy for MAPT
Antisense oligonucleotides can be used to reduce tau protein expression. Tau aggregation inhibitors include curcumin and the methylene blue derivative LMTX. Microtubule stabilizers such as TPI-287 and NAP can be used to compensate for the loss of tau's normal microtubule-stabilizing function. Modulators of autophagy or proteasomal degradation can promote the clearance of pathological tau protein. Active and passive immunotherapies use antibodies to target pathological tau protein intracellularly or extracellularly , promoting its degradation and clearance.
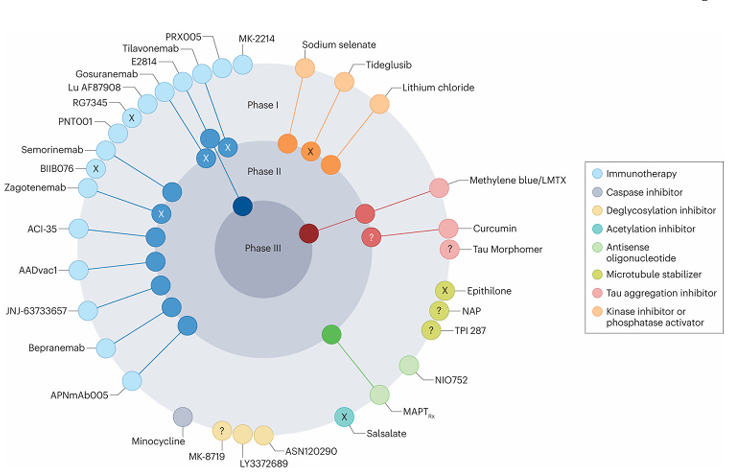
(Data source : Congdon EE , et al. Nat Rev Neurol . 2023)
Etalanetug is a monoclonal antibody developed by Eisai that targets TAU . Its primary mechanism of action is as a TAU inhibitor , used to treat Alzheimer's disease and cognitive impairment . It was first approved for Phase 3 clinical trials on December 22 , 2021 .

(Data source: Rawal S , et al. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 2025)
MK-2214 is a monoclonal antibody developed by Merck that targets Tau . Its primary mechanism of action is as a Tau inhibitor , intended for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease and cognitive impairment . It was first approved for Phase 2 clinical trials on July 16 , 2025. Tau antibodies inhibit abnormal Tau protein aggregation and clearance by binding to Tau aggregates , endocytosis , and proteasomal degradation, as well as TRIM21-mediated proteasomal degradation . They are one of the immunotherapy strategies for Alzheimer's disease and other Tauopathies .

(Data source: Congdon EE , et al. Nat Rev Neurol . 2023)
VY-7523 is a tau- targeting monoclonal antibody developed by Voyager Therapeutics . Its primary mechanism of action is as a tau inhibitor , intended for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease, Pick's disease-related dementia, and progressive supranuclear palsy . It was first approved for Phase 2 clinical trials on March 3, 2025 .
PRX-005 (BMS-986446) is a tau-targeting monoclonal antibody developed by Prothena . Its primary mechanism of action is as a tau modulator, intended for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease . It was first approved for Phase 2 clinical trials on March 20, 2024 .
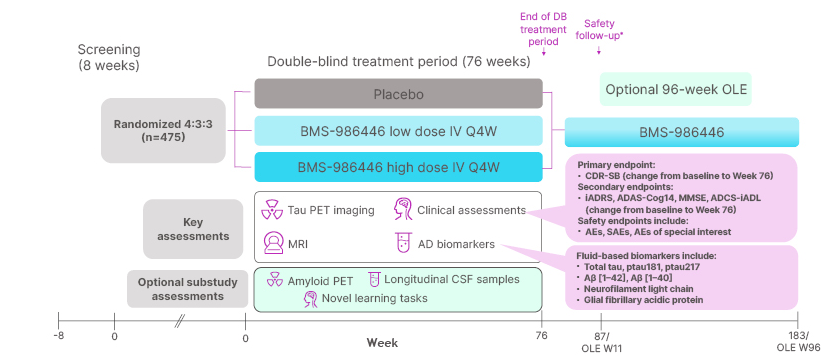
(Data source: Christopher H, et al. The Journal of The Alzheimer 'S Association 2025)
