Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2) is a tyrosine protein kinase, also known as fetal liver kinase 1 (FLK-1).
Kinase insert domain receptor (KDR). VEGFR2 serves as a cell surface receptor for VEGFA, VEGFC, and VEGFD. It plays a crucial role in regulating angiogenesis, vascular development, vascular permeability, and embryonic hematopoiesis. It promotes endothelial cell proliferation, survival, migration, and differentiation.
VEGFR2 expression distribution
VEGFR2 is mainly expressed in mesothelial cells, glial cells, endothelial cells, adipocytes, and lymphatic endothelial cells, and is particularly expressed in tissues with active metabolism or angiogenesis (such as lung, heart, placenta, and retina).

The tyrosine kinase domain (TKD) is the most conserved region in VEGFRs. The protein kinase core of VEGFR-2 has a two-lobed structure, with the active center formed between the two lobes. At the N-terminus of the intracellular tyrosine kinase domain, a hydrophobic pocket containing a glycine-rich ATP phosphate-binding loop (GXGXXG, 841-846 aa) is located within a β-sheet structure. At the C-terminus of the TKD, several α-helical structures, including a catalytic loop (HRDLAARN , 1026-1033 aa ) and an activation loop (A loop , 1045-1075 aa ), play a key role in the catalytic properties of VEGFR-2 .
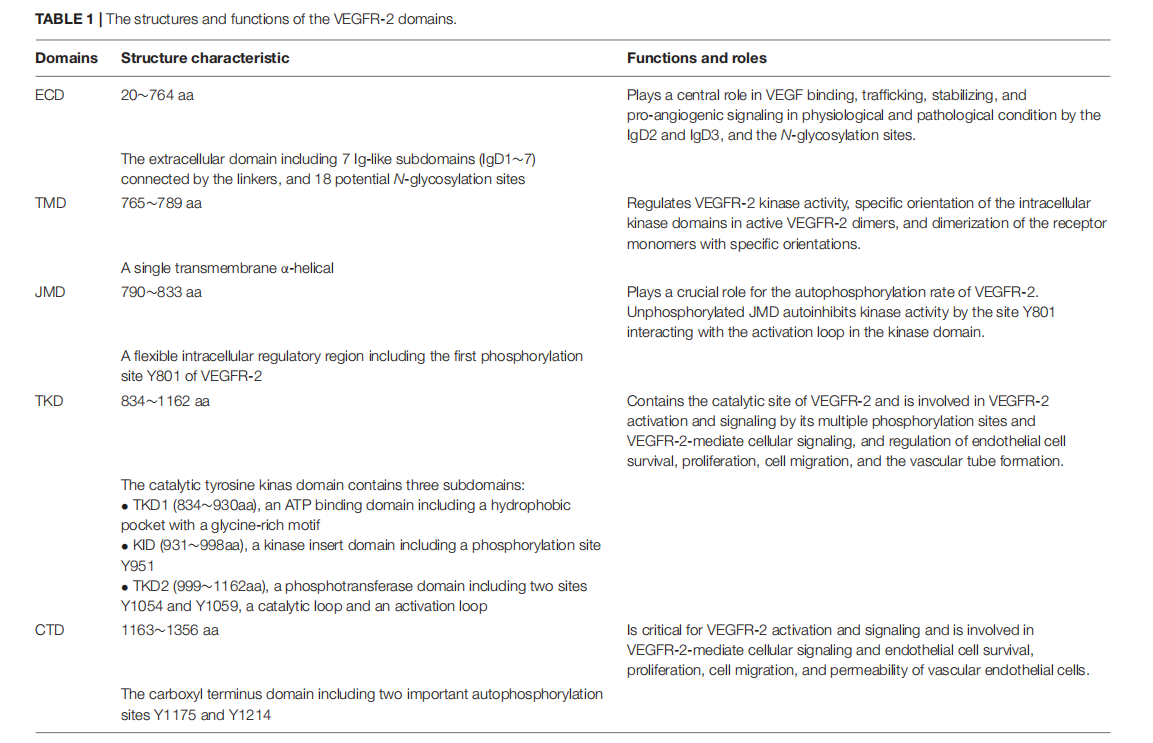
( Data source: Wang X. Front Cell Dev Biol . 2020)
VEGFR2 signaling pathway and regulation
VEGF activates VEGFR-2 homodimers. Upon VEGF binding to VEGFR-2, key tyrosine residues within the kinase domain become phosphorylated ( key phosphorylation sites : Y1175 , Y951 , and Y1214 ) , mediating downstream signaling pathways such as the PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway, the RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK pathway, the SRC-FAK pathway, and the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway. These intracellular pathways mediate angiogenesis by regulating endothelial cell proliferation, survival, motility, and vascular permeability. Angiogenesis plays a crucial role in the progression of many malignancies, retinal diseases, and vascular and neurological disorders.

( Data source: Wang X. Front Cell Dev Biol . 2020)
VEGFR2 -targeted therapy
Olinvacimab is a monoclonal antibody targeting VEGFR2, developed by pharmabcine . It is an anti-angiogenic antibody that neutralizes the VEGF/VEGFR2 pathway, thereby inhibiting tumor growth and metastasis. It blocks the binding of all VEGFR ligands (such as VEGF-A, VEGF-C, and VEGF-D) to VEGFR2 . To obtain nutrients and oxygen for growth, tumor cells release these VEGF ligands, which promote angiogenesis (the formation of new blood vessels), thereby enhancing tumor blood supply. Olinvacimab binding to VEGFR2 results in the inhibition of VEGF-mediated tumor angiogenesis. Pharmabcine has multiple global clinical studies involving olinvacimab ongoing. In addition to the olinvacimab and pembrolizumab combination trial in mTNBC (triple-negative breast cancer), which dosed the first patient in December 2021, a Phase 2a clinical trial investigating olinvacimab monotherapy in patients with bevacizumab-unresponsive rGBM (recurrent glioblastoma) is ongoing at multiple sites in the United States and Australia. Two Phase 1b trials in mTNBC and rGBM have already been completed in the combination of olinvacimab and pembrolizumab.
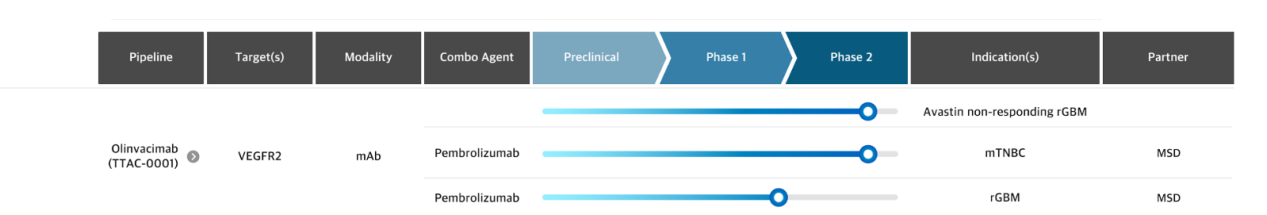
(Data source: pharmabcine official website)
Pulocimab ( AK109 ), a monoclonal antibody targeting VEGFR2, is being developed by Zhongshan Kangfang and is currently in Phase 3 clinical trials. Pulocimab targets the extracellular domain (D3-D4) of VEGFR2, inhibiting the binding of VEGF-A/-C/-D and blocking downstream pro-angiogenic signaling (such as the PI3K/AKT and MAPK pathways). NCT05142423 is an open-label , multicenter, Phase Ib/II clinical study evaluating the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and antitumor activity of Pulocimab in combination with the PD-1 antibody Penpulimab (AK104) in patients with advanced solid tumors. NCT06341335 is a randomized, double-blind, Phase 3 study comparing Cadonilimab (AK104) combined with Pulocimab (AK109) and paclitaxel versus paclitaxel in patients with advanced gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma who have failed first-line immunochemotherapy.

(Data source: Akeso official website)
Ramucirumab ( Cyramza® ) is a fully humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody and a receptor antagonist that targets the extracellular domain of VEGFR- 2, thereby blocking its interaction with vascular endothelial growth factor ligands (VEGF-A, -C, and -D) and inhibiting receptor activation. It was approved in the US on April 21, 2014 , the first time it has been approved in the US for advanced gastric cancer or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma.
