The endothelin-1 receptor (EDNRA) is a multi-pass transmembrane protein belonging to the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily (GPCRs). It is primarily distributed in vascular smooth muscle cells and primarily mediates the biological effects of endothelin-1 (ET-1) and endothelin-2 (ET-2). It is crucial for processes such as vasoconstriction and cell proliferation, playing a central role in the endothelin signaling pathway.
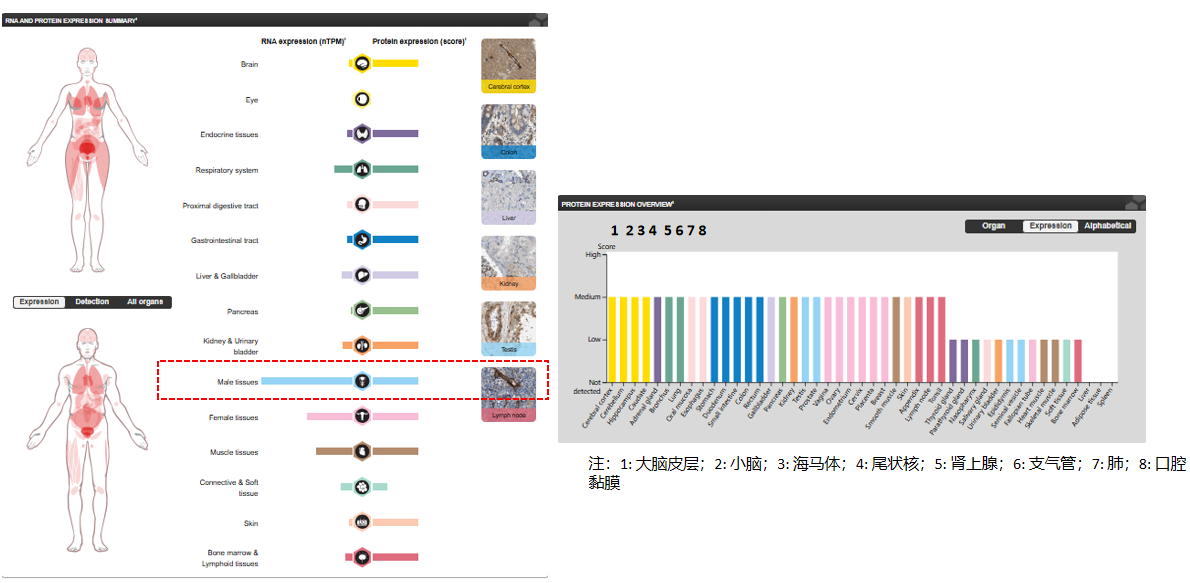
Expression distribution of EDNRA
EDNRA comprises multiple isoforms, of which isoforms 1, 3, and 4 are expressed in various tissues, with the highest expression levels in the aorta and cerebellum, followed by the lung, atrium, and cerebral cortex. Expression is lower in the placenta, kidney, adrenal gland, duodenum, colon, ventricle, and liver, and is absent in umbilical vein endothelial cells. Within the placenta, isoforms 1, 2, 3, and 4 are expressed in the villi and their stem vessels.
(Data source: Uniprot)
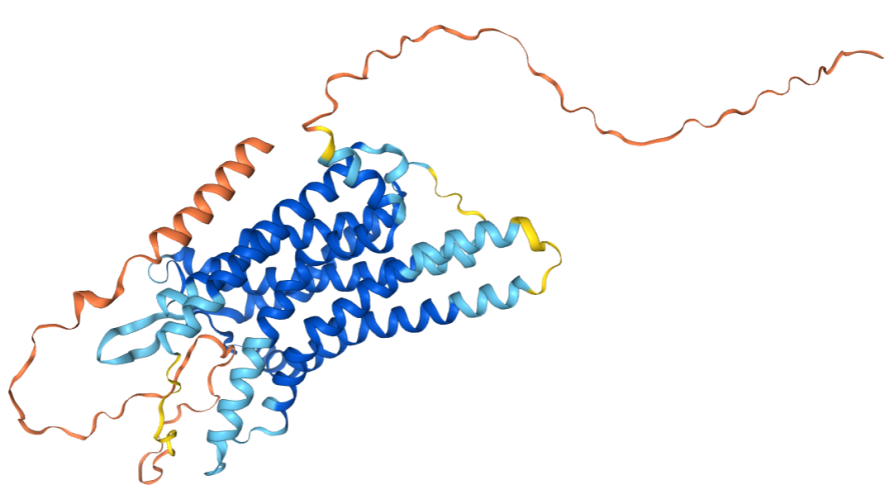
Structure of EDNRA
EDNRA is a multi-channel receptor transmembrane protein encoded by the EDNRA gene with a length of 427 AA and a molecular weight of approximately 48.7 kDa. It contains extracellular, transmembrane and intracellular domains. It is a member of the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily (GPCRs) and mainly mediates the biological effects of endothelin-1 (ET-1) and endothelin-2 (ET-2). It is crucial for processes such as vasoconstriction and cell proliferation.
N-terminal extracellular domain: Located on the outside of the cell membrane, it usually contains conserved cysteine residues, which may participate in the formation of disulfide bonds and stabilize the extracellular structure.
Seven transmembrane domains: Contains seven hydrophobic α-helices (TM1-TM7) that cross the cell membrane. These helices form a pocket-like structure, which is the main site for ligand (endothelin) binding.
C-terminal intracellular domain: Located in the cytoplasm, it contains multiple serine/threonine phosphorylation sites and may be involved in the interaction with other signaling proteins or scaffold proteins.
(Data source : AlphaFold)
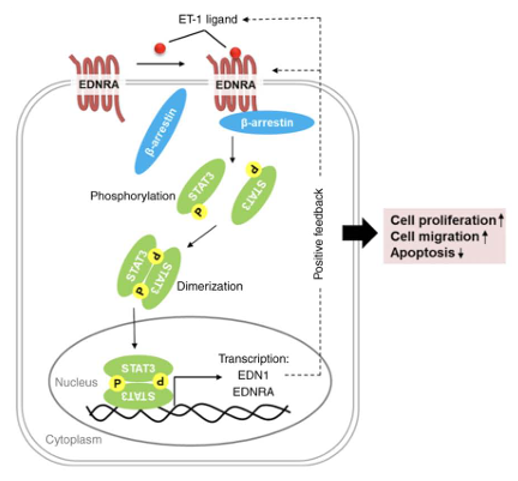
EDNRA signaling pathway
Gq/11 pathway activation: EDNRA primarily couples to Gq/11 proteins, activating phospholipase Cβ (PLCβ), which hydrolyzes phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate (PIP₂) to generate inositol triphosphate (IP₃) and diacylglycerol (DAG). IP₃ triggers calcium release from the endoplasmic reticulum, and DAG activates protein kinase C (PKC), collectively regulating cell contraction, proliferation, and gene expression.
Receptor internalization and recycling: Upon EDN1 binding, EDNRA undergoes a conformational change and is internalized into the cell. Unlike EDNRB (type B receptor), EDNRA is often recycled to the cell membrane after internalization, prolonging the signaling duration, whereas EDNRB is targeted for degradation.
(Data from Jiaqi Fu , et al. Front Cell Neurosci . 2023)
EDNRA and Disease
EDNRA (endothelin receptor type A) is a member of the G protein-coupled receptor family that primarily mediates the vasoconstrictive, cell proliferation, and fibrotic effects of endothelin-1 (ET-1). Its dysfunction can lead to multisystem diseases by affecting developmental signaling pathways, vascular tone regulation, and tissue remodeling.
Auriculocondylar Syndrome (ACS): EDNRA heterozygous frameshift mutation (e.g., exon5: c.811_812insT, p.T271fs) or missense mutations in EDNRA disrupt the EDN1-EDNRA-DLX5/6-Hand2 signaling pathway, affecting embryonic pharyngeal arch development and leading to abnormal mandibular differentiation. Clinical manifestations include micrognathia, mandibular condylar hypoplasia, and the characteristic "question mark ear" deformity (absence of the upper part of the auricle).
Intracranial Aneurysm (IA): SNPrs6841581, located in the 5'-UTR region of EDNRA, enhances EDNRA expression, promotes vascular endothelial dysfunction and vascular wall remodeling, and increases the risk of tumor formation.
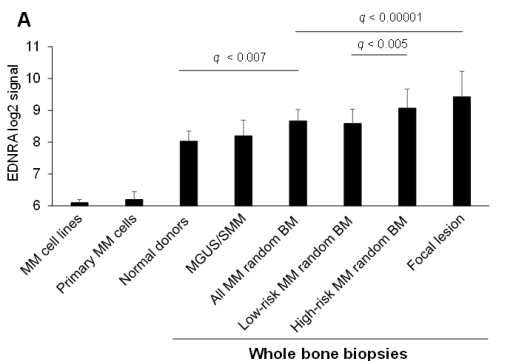
Multiple myeloma: EDNRA is highly expressed in osteoclast precursor cells. Upon activation, it upregulates the RANKL/NFATc1 pathway, promoting bone resorption. Silencing EDNRA or the upstream transcription factor MEF2A can inhibit bone loss.
(Data source: Ling W, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2023)
Kidney disease: ETₐ receptors mediate the kidney damage pathway (vasoconstriction → fibrosis → proteinuria), and ETᵦ receptors activate the protective pathway (vasodilation → sodium and water excretion), forming a bidirectional regulatory mechanism.
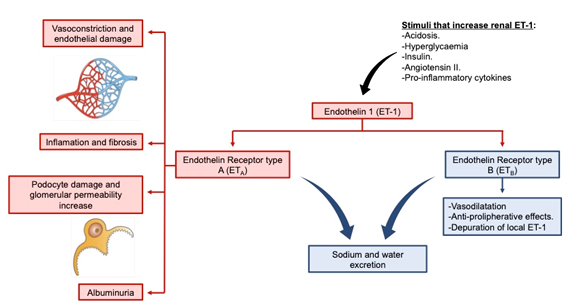
(Data source: Martínez DI , et al. nt J Mol Sci. 2023)
Targeted therapy for EDNRA
Getagozumab , a monoclonal antibody targeting EDNRA, is being developed by Hongyun Huaning (Hangzhou) Biopharmaceutical Co. , Ltd. Its primary mechanism of action is as an EDNRA antagonist, binding with high affinity to the extracellular domain of EDNRA and blocking the binding of endothelin-1 (ET-1) to EDNRA. It is intended for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). It was approved for Phase 2 clinical trials in China on January 30, 2022.
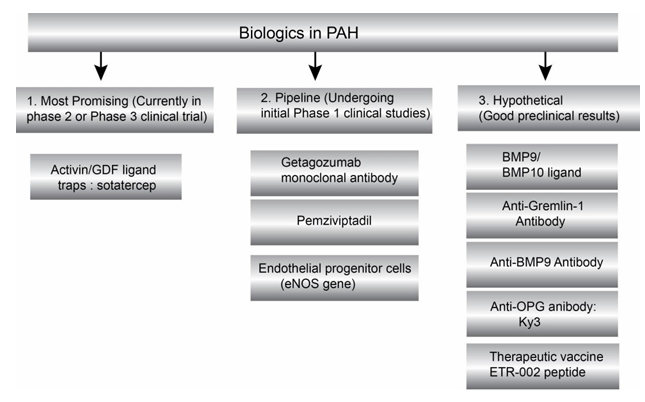
(Data source: Hye T , et al. J Drug Target. 2023)
WO2022262733 is a bispecific antibody drug targeting EDNRA and CD3, developed by Hongyun Huaning (Hangzhou) Biopharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Its primary mechanism of action is as an EDNRA antagonist and a CD3 inhibitor, intended for the treatment of tumors. The drug is currently in the drug discovery phase.
HH-103 is a monoclonal antibody targeting EDNRA, developed by Hedgehog Co, Ltd. Its primary mechanism of action, similar to getagozumab , is as an EDNRA antagonist for the treatment of solid tumors. It is currently in the preclinical stage.
Patecibart ,developed by Abinscience, is a humanized immunoglobulin IgG4-kappa monoclonal antibody targeting EDNRA. Its primary mechanism of action is as an EDNRA antagonist, intended for the treatment of tumors. The current clinical stage is unknown.
