LEPR expression distribution
LEPR isoform A is expressed in fetal liver, hematopoietic tissue, and the choroid plexus. In adults, its highest expression is in the heart, liver, small intestine, prostate, and ovary, with lower levels in the lung and kidney. Isoform B is highly expressed in the thalamus and also in skeletal muscle; it can be detected in the fundic and antral epithelial cells of the gastric mucosa. Isoforms B and A are expressed in natural killer (NK) cells.
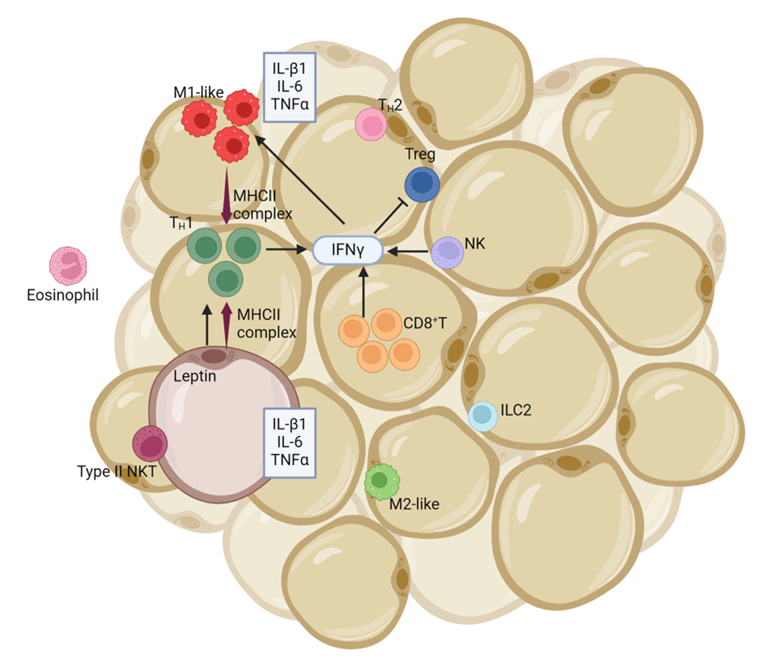
(Data source : Abdulla A , et al. J Natl Cancer Cent . 2024)
The structure of LEPR
LEPR is encoded by the LEPR gene, which is 1165 aa in length and has a molecular weight of approximately 132,4 kDa type I transmembrane protein, composed of three parts: intracellular region, transmembrane region and extracellular region , and generates multiple isomers (such as long LEPR-b, short LEPR-a/c/d/f, soluble LEPR-e) through selective splicing.
Extracellular region ( 22-839 aa ): a) Cytokine receptor homology 2 (CRH2) domain: This is the key region for leptin binding. It contains two conserved disulfide bonds, responsible for specific recognition and binding of leptin molecules. b) Immunoglobulin-like domain (Ig-like domain): Located before the CRH2 domain, it may be involved in stabilizing the leptin-receptor complex or interacting with other accessory proteins. c) Two fibronectin type III domains (FnIII domains): This is a hallmark structure of class I cytokine receptors, located close to the cell membrane and crucial for receptor dimerization (the binding of two receptors to form a dimer) and signal transduction.
Transmembrane region (840-862 aa): composed of an α-helix, its main function is to anchor the receptor on the cell membrane and transmit conformational changes in the extracellular region to the intracellular region.
Cytoplasmic region (863-1165 aa): a) This is the core of signal transduction. The intracellular domain of LEPR is not enzymatically active, but it recruits and activates downstream tyrosine kinases. b) Its length and amino acid sequence are key to distinguishing different LEPR isoforms (primarily the long isoform LepRb and the short isoform). The long isoform LepRb has the longest intracellular domain and contains multiple conserved motifs for signal recruitment, making it the isoform that plays the primary physiological role.
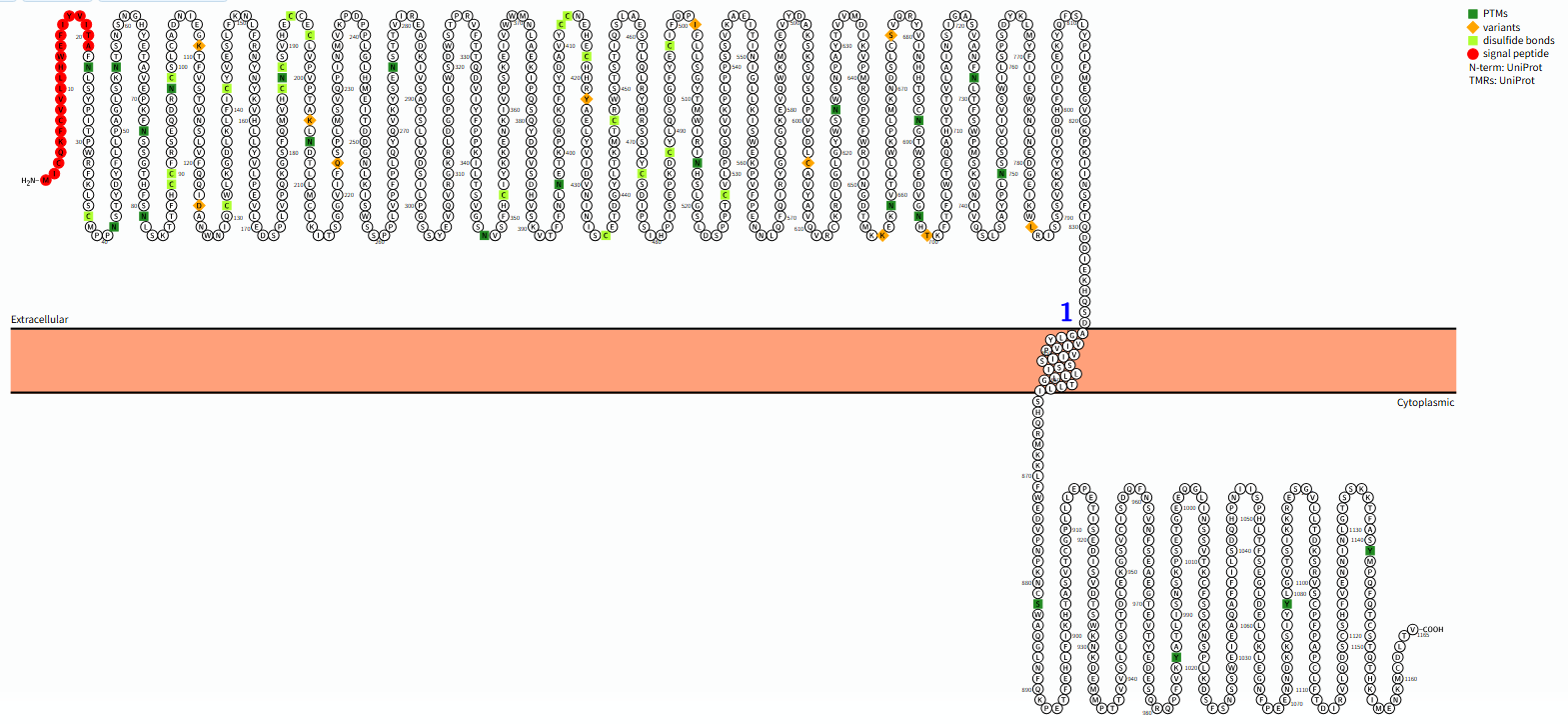
(Data source : protter)
LEPR signaling pathway
a) JAK-STAT pathway: Leptin binds to the extracellular domain of the receptor, leading to receptor dimerization. Upon receptor dimerization, the intracellular domain recruits and activates the bound JAK2 (Janus Kinase 2) tyrosine kinase. Activated JAK2 phosphorylates specific tyrosine residues in the receptor intracellular domain, providing docking sites for downstream signaling proteins. The most important signaling protein is STAT3 (Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3).
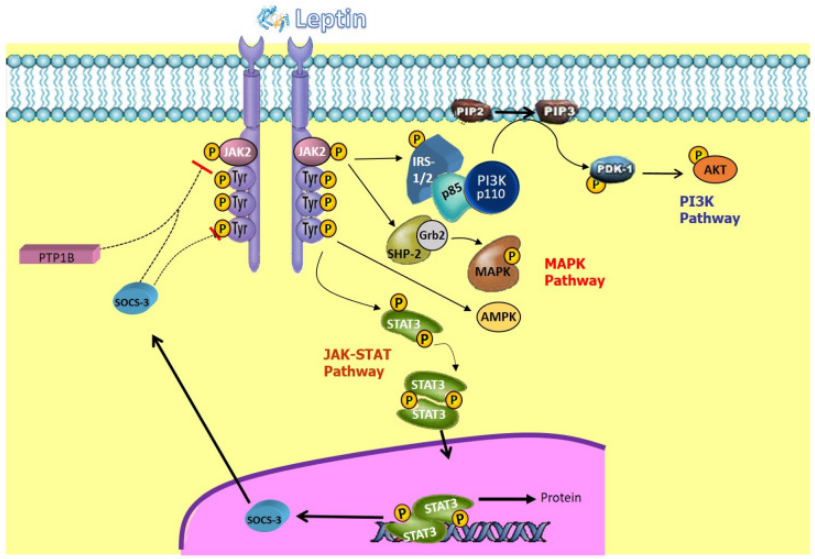
(Data source : Vilariño-García T, et al. Int J Mol Sci . 2024)
b) PI3K-AKT pathway: This pathway is activated more indirectly. On the one hand, JAK2 can phosphorylate insulin receptor substrate (IRS) proteins, which recruit and activate PI3K. On the other hand, the gene transcript of STAT3 may also indirectly influence this pathway.
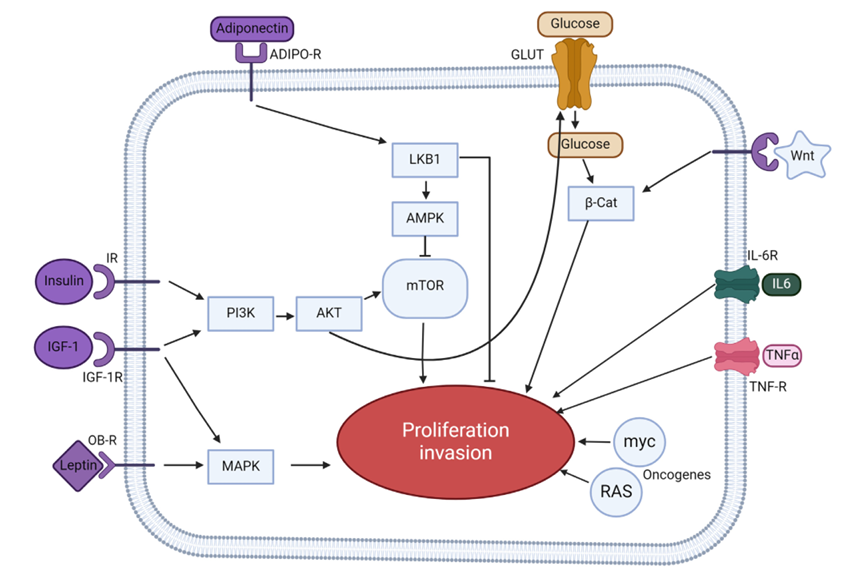
(Data source: Abdulla A , et al. J Natl Cancer Cent . 2024)
LEPR and disease
Severe early-onset obesity: This is often caused by congenital LEPR gene mutations, which lead to complete or partial loss of receptor function. Leptin cannot send "fullness" signals, causing the brain to mistakenly believe the body is hungry.
Cardiovascular Disease: Normal: Moderate circulating leptin levels, normal adipocyte morphology, and a healthy heart. When lipodystrophy develops, adipocyte apoptosis leads to insufficient leptin secretion, ultimately causing cardiovascular disease. When obesity develops, adipocyte hypertrophy causes leptin resistance (leptin signaling is ineffective despite high leptin levels), ultimately leading to cardiovascular disease.
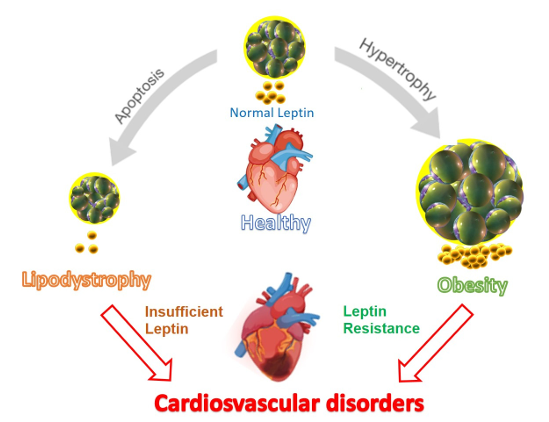
(Data source: Vilariño-García T, et al. Int J Mol Sci . 2024)
Leptin/insulin resistance: After leptin activates its receptor (LepR), it regulates appetite genes such as POMC/AGRP through the JAK-STAT3 pathway and activates the PI3K-Akt pathway to inhibit FoxO1. This pathway cross-talks with insulin receptor (InsR) signaling. In leptin resistance, LepR dysfunction leads to insufficient PI3K-Akt activation. This weakens the inhibition of FoxO1, causing appetite disorders and increased food intake. It also reduces the inhibitory effect of AMPK on mTOR, leading to overactivation of the mTOR pathway and promoting lipid synthesis and metabolic disorders. Furthermore, impaired leptin signaling further interferes with insulin signaling, creating a vicious cycle of leptin resistance and insulin resistance.
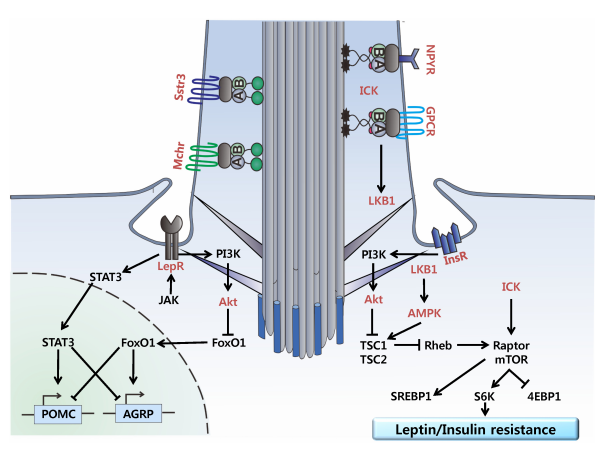
(Data source: Lee H, et al. BMB Rep. 2015)
In the field of Breast Cancer: a ) Leptin binds to the LEPR and, through the MAPK/STAT3 pathway, promotes CYP19A1 transcription, enhancing aromatase activity and converting androgens to estradiol. Estradiol then enters the nucleus and binds to ERα, activating cancer-related genes. b) Leptin binds to the LEPR and, through the STK11-AMPK-CRTC2 pathway, upregulates CYP19A1, similarly driving aromatase-mediated estradiol synthesis and thus supporting breast cancer progression.
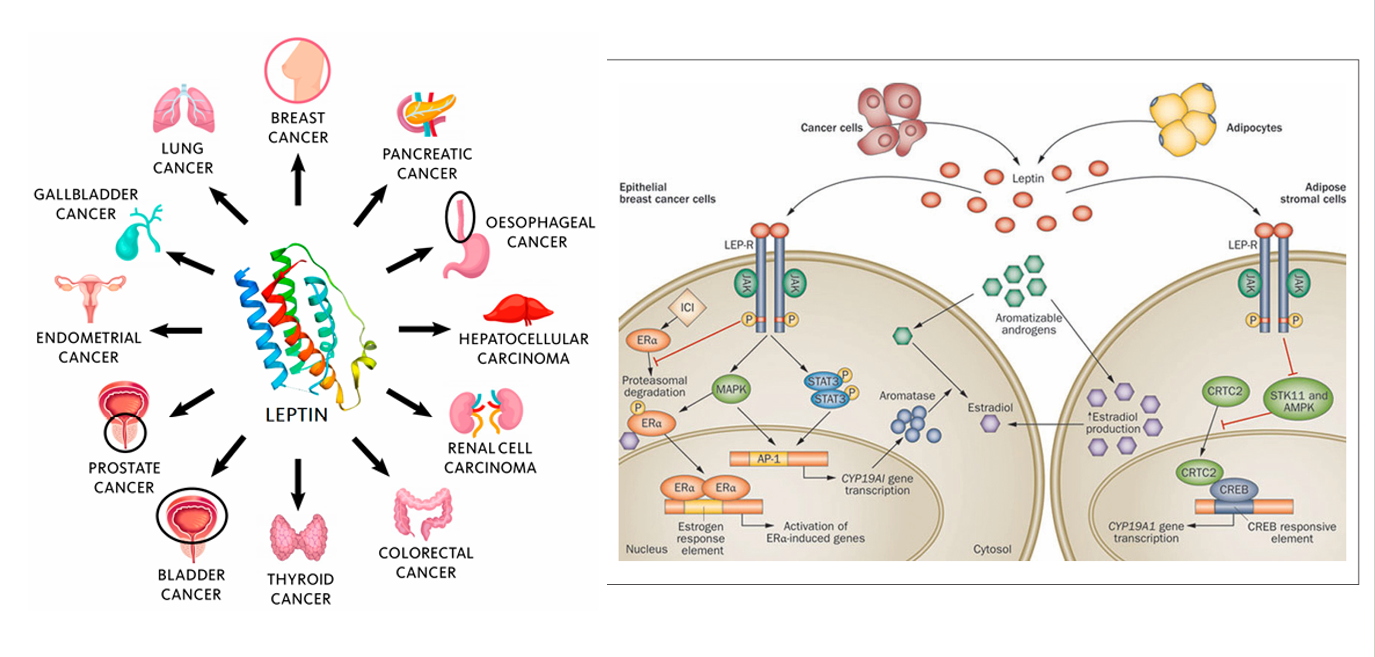
(Data source: Jiménez-Cortegana C, et al. Biomolecules. 2021; right: Dutta D, et al. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2012)
Targeted therapy for LEPR
Mibavademab is a monoclonal antibody targeting LEPR, co-developed by Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. Its primary mechanism of action is as a LEPR agonist, enhancing its activity by binding to LEPR and ameliorating metabolic abnormalities. It is intended for the treatment of congenital generalized lipodystrophy and obesity. It was approved for Phase 3 clinical trials on December 16, 2024.
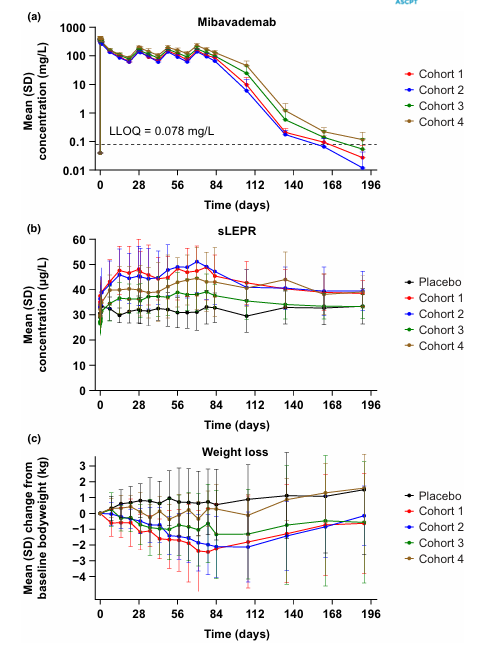
(Data source: Gewitz A, et al. Clin Transl Sci . 2024)
The Anti-LEPR/GP130 bispecific antibody, developed by Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, targets LEPR and IL6RB . Its primary mechanism of action is as a LEPR agonist and an IL6RB regulator. By targeting LEPR and IL6RB (GP130), it modulates metabolic and inflammatory pathways for the treatment of obesity and endocrine and metabolic diseases. It is currently in the preclinical stage.
Recombinant methionyl human Fc-leptin is a Leptin-targeting Fc fusion protein developed by Amgen. Its primary mechanism of action is as a Leptin antagonist, intended for the treatment of obesity. The current clinical stage is unknown.
CV-08-01, a fusion protein drug targeting LEPR developed by Cellivery Therapeutics , acts as a LEPR antagonist , inhibiting tumor growth or metabolic abnormalities by blocking LEPR signaling. It is currently in the final development phase of its pipeline.
