Solute Carrier Family 1 Member 5 (SLC1A5/ASCT2) is a transmembrane protein that functions as a sodium-dependent neutral amino acid transporter. Encoded by the SLC1A5 gene in humans, it is primarily responsible for the cellular uptake of small and medium-sized neutral amino acids, with a particular affinity for glutamine.
SLC1A5 Expression distribution
SLC1A5 is specifically expressed in the liver, kidney, small intestine, brain (particularly in endothelial cells and astrocytes of the blood-brain barrier), testes, placenta, and activated lymphocytes. Its primary function in these tissues is to participate in inter-organ amino acid distribution, absorption, and recycling. Expression in tumor tissues: It is overexpressed in various solid tumors, and its expression level often correlates with tumor malignancy, stage, and poor prognosis.
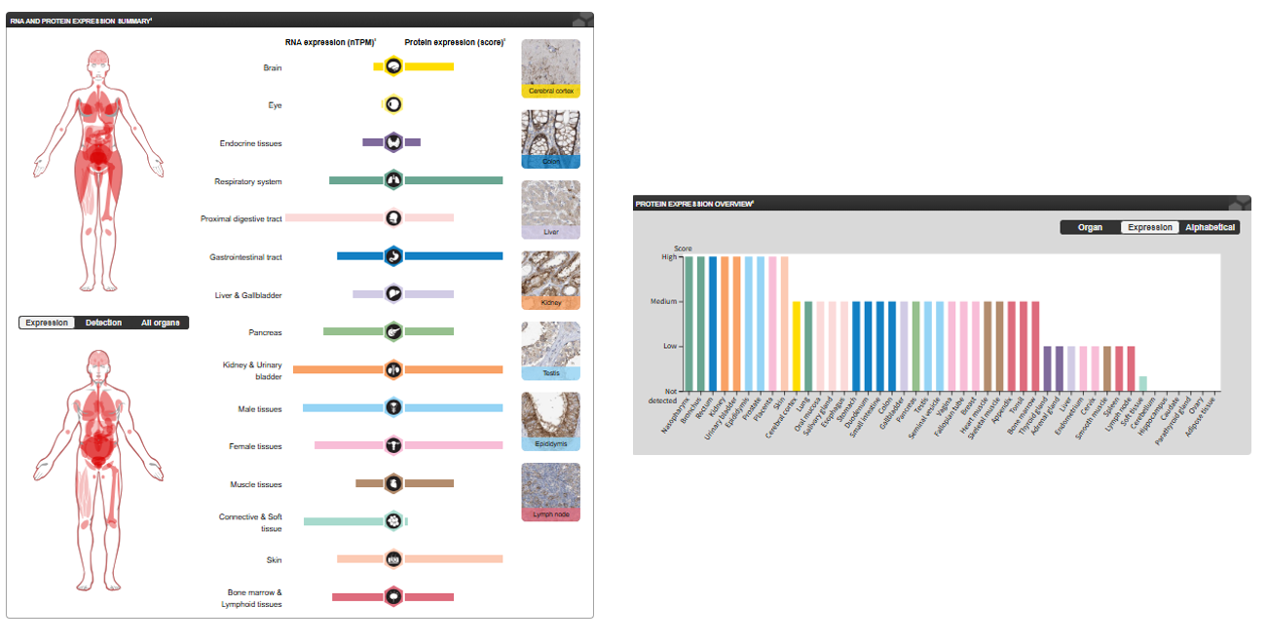
(Data source : proteinatlas)
SLC1A5 Structure
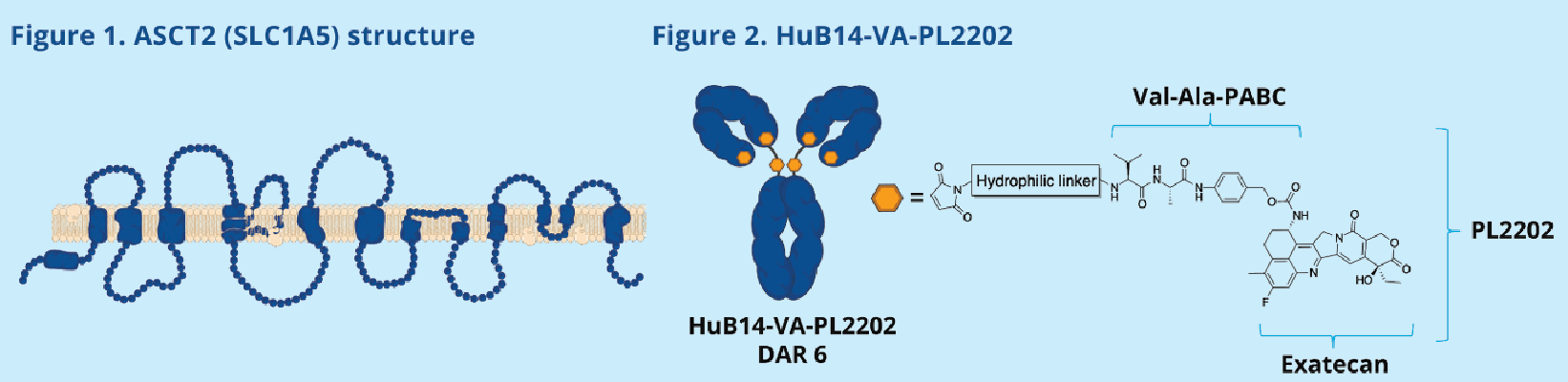
SLC1A5 The length 258 of SLC1A5 the gene encoding aa , with a molecular weight of about 28 kDa type III transmembrane protein, composed of three parts: intracellular region, transmembrane region and extracellular region.
Transport domain: responsible for the binding and conformational changes of substrates (such as glutamine). The key HP2 loop (intracellular loop) undergoes conformational rearrangement during substrate recognition and is directly involved in the formation of the substrate binding pocket.
Scaffold domain: It is connected to the transport domain through the ECL2a loop (extracellular loop2a), providing structural support for the rigid movement of the transport domain and ensuring the coordinated movement between domains in the transport cycle.
Transmembrane region (69-86 aa; 107-131 aa; 143-169 aa): composed of three α-helices, its main function is to anchor the receptor on the cell membrane and transmit conformational changes in the extracellular region to the intracellular region.
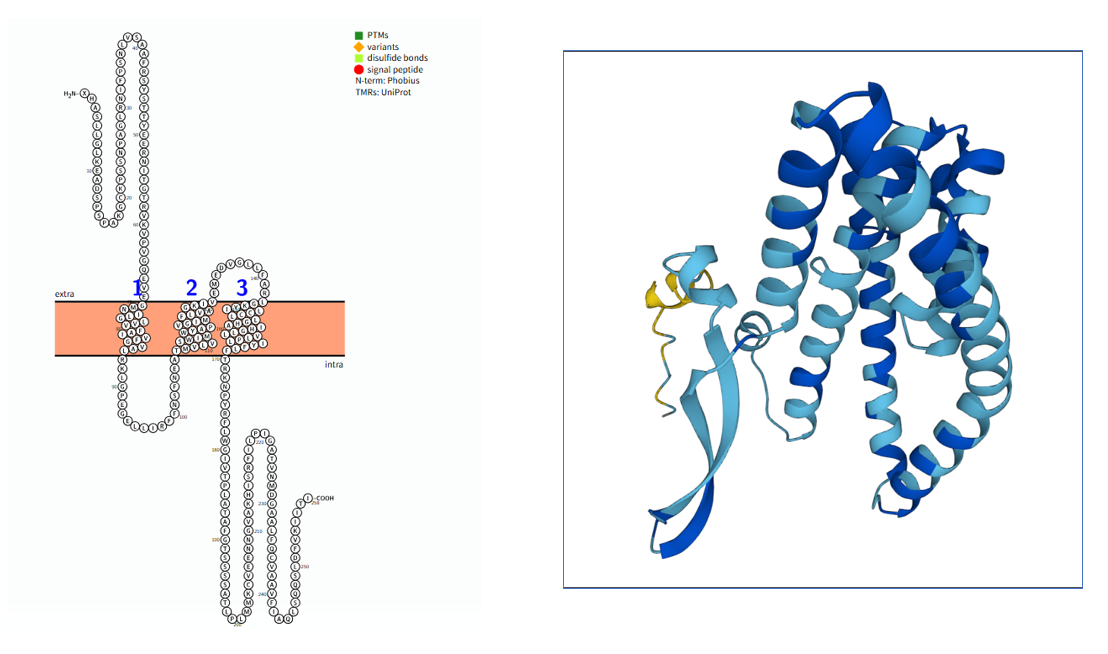
(Data source: protter)
SLC1A5 signaling pathways
mTORC1 (target of rapamycin complex 1) is a core signaling hub that allows cells to sense nutrient, energy, and growth factor status and regulate cellular anabolism (such as protein synthesis and lipid synthesis) and cell growth. Amino acids are essential signals for mTORC1 activation.
a) mTORC1 activation pathway: SLC1A5 mediates glutamine (Gln) uptake, which is then metabolized to α-ketoglutarate (α-KG). This activates mTORC1 through Rag GTPases, which in turn promotes phosphorylation of downstream target proteins (such as S6K1 and 4EBP1), driving cell proliferation and protein synthesis. This pathway is often overactivated in tumor cells. For example, in pancreatic cancer, IGF2BP2 stabilizes SLC1A5 mRNA through m⁶A modification, enhancing glutamine uptake and thus mTORC1 activation.
(Data source : Chen C et al. Front Pharmacol. 2022)
b) c-Myc transcriptional regulation: The proto-oncogene c-Myc is a key transcription factor for SLC1A5. c-Myc directly binds to the promoter region of the SLC1A5 gene, significantly upregulating its transcription and protein expression. This allows cancer cells to obtain more glutamine, which is essential for their rapid proliferation.
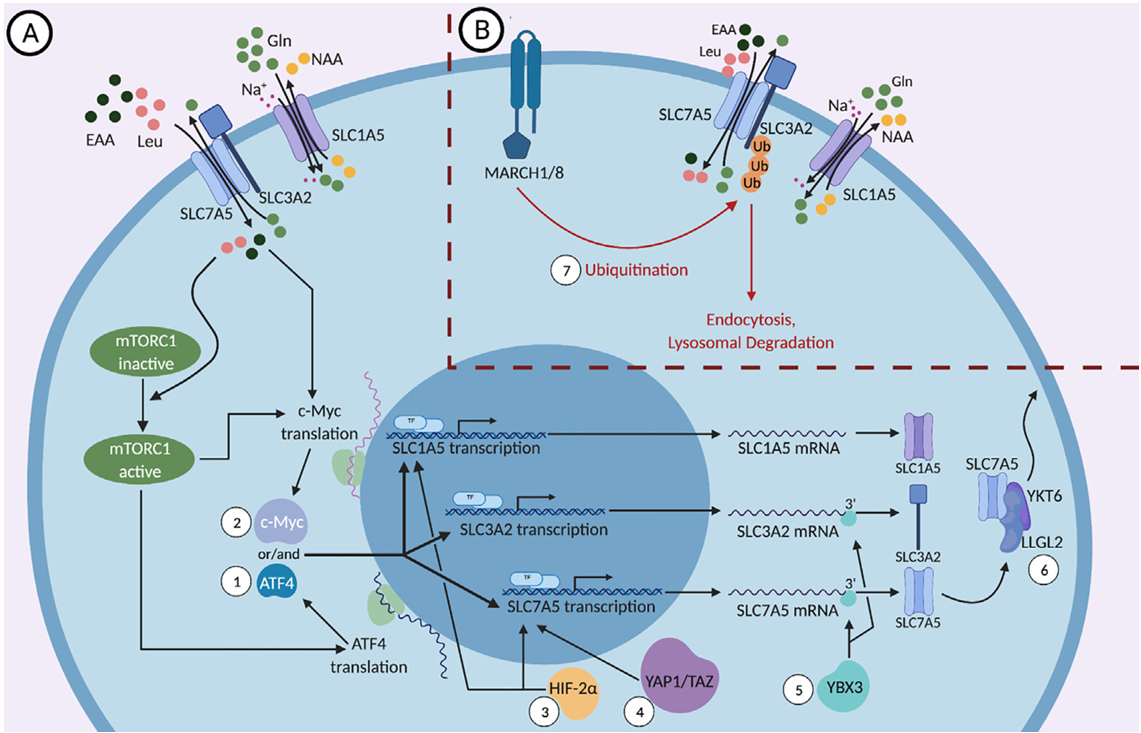
(Data source: Nachef M et al. Front Immunol. 2021)
SLC1A5 and disease
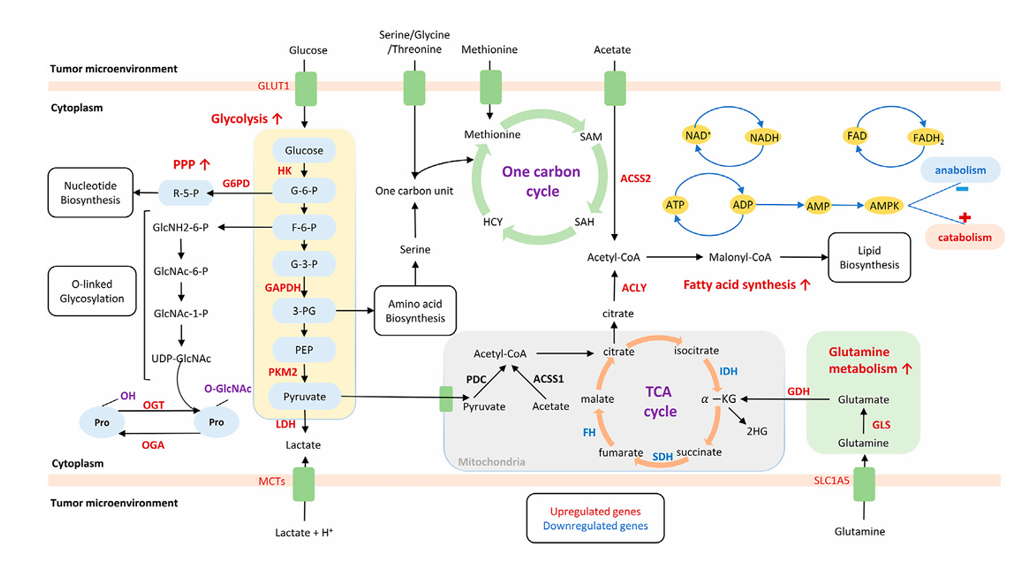
Ferroptosis in cancer cell metabolism: A non-apoptotic, iron-dependent form of cell death caused by lipid peroxidation, termed ferroptosis. Cell membrane transport systems (such as System Xc⁻, GLUT1, and TFRC) mediate the uptake of substances such as cystine, glucose, and iron, providing a foundation for glutathione (GSH) synthesis, energy metabolism, and iron homeostasis. Metabolic pathways such as the PPP generate NADPH to support antioxidant defense, and O-GlcNAc modification regulates multiple key proteins. Iron pool levels are influenced by processes such as mitochondrial autophagy and ferritin autophagy. These systems jointly regulate lipid peroxidation and the GSH–ROS balance, thereby integrally determining ferroptosis sensitivity.
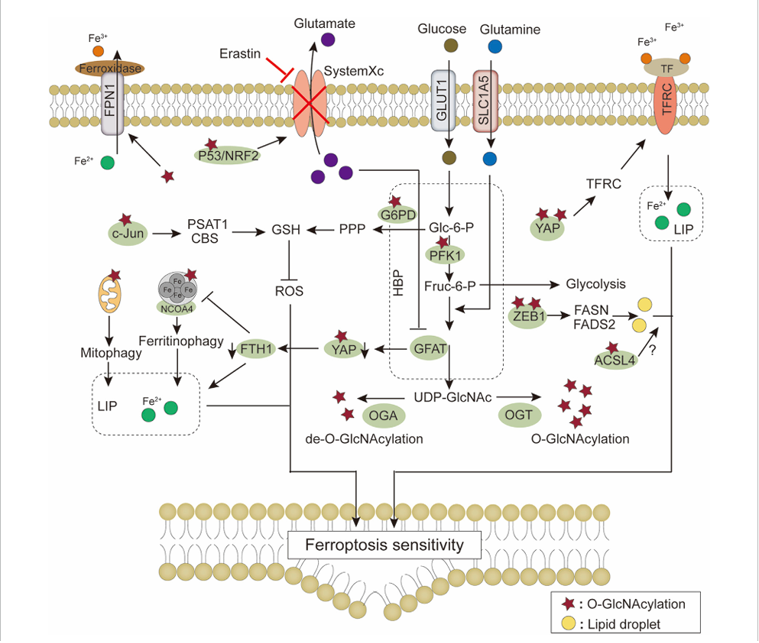
(Data source: Zhang H et al. Front Mol Biosci. 2023)
Cardiovascular disease (CVD): SLC1A5 is a cell membrane transporter protein primarily involved in glutamine uptake. It collaborates with SystemXc (a system mediating glutamate/cysteine exchange) to influence intracellular glutathione (GSH) synthesis (GSH is a key antioxidant molecule that scavenges reactive oxygen species (ROS)). By regulating GSH levels and ROS balance, SLC1A5 ultimately influences susceptibility to ferroptosis (ferroptosis is closely related to lipid peroxidation and ROS accumulation; GSH deficiency increases susceptibility to ferroptosis).
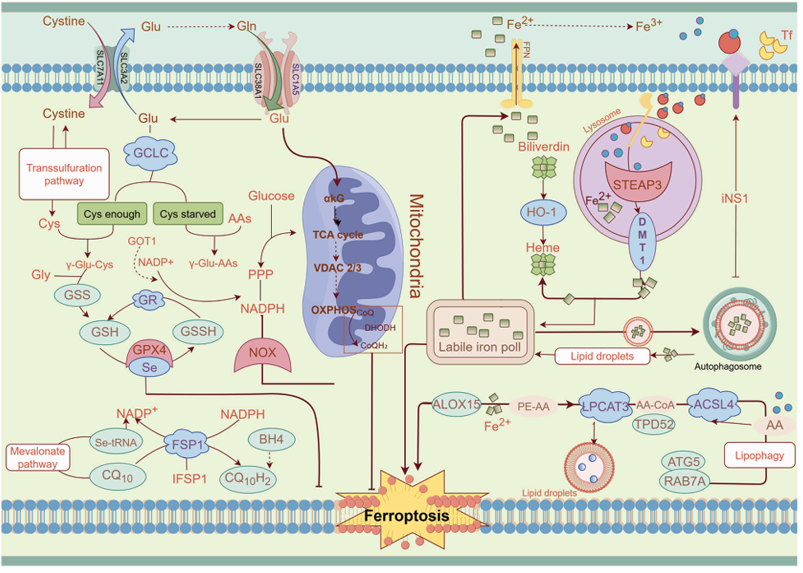
(Data source: Qin S et al. Int J Mol Med. 2025)
Human chondrosarcoma cells, amphiregulin (AR) activates the MEK–ERK signaling pathway, phosphorylating and activating the transcription factor Nrf2, thereby promoting the expression of multiple target genes, including SLC1A5. SLC1A5-mediated increased glutamine uptake, which is broken down into glutamate by GLS and then enters the mitochondria, enhancing TCA cycle metabolic flux and ultimately generating large amounts of NADPH. This molecule effectively scavenges cisplatin-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS), mitigating oxidative damage, thereby significantly enhancing cellular antioxidant capacity and conferring cisplatin resistance.
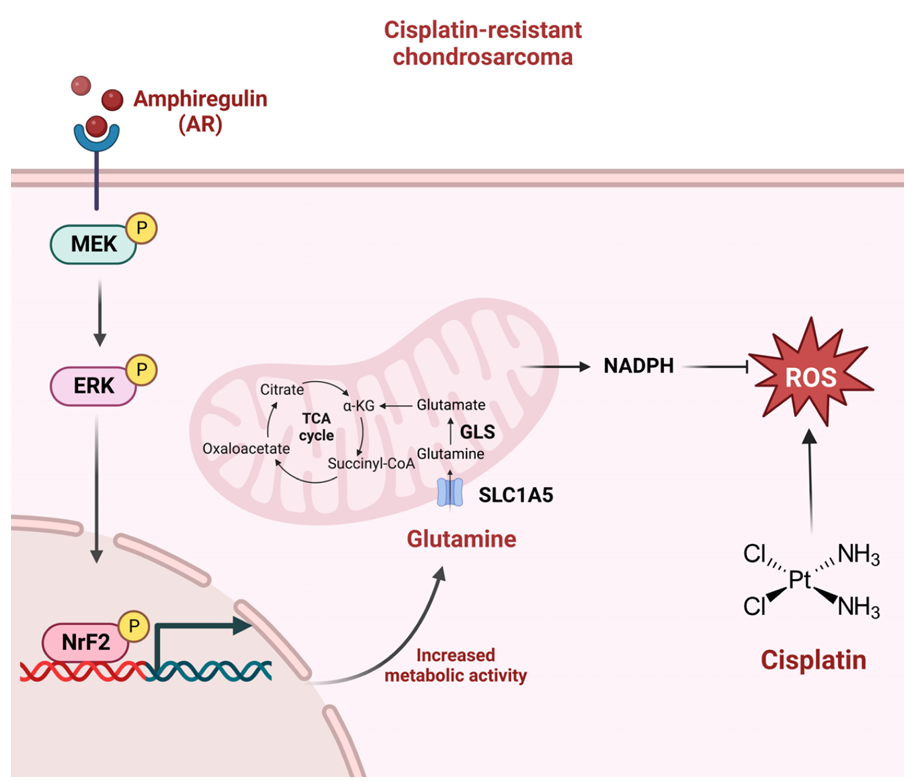
(Data source: Wu YY et al. Int J Biol Sci. 2023)
In the field of immunogenic cell death (ICD), tumor cells absorb nutrients through membrane transporters (such as SLC1A5/SLC7A5 and glucose transporters), efficiently obtaining energy and NADPH through glycolysis, the pentose phosphate pathway, the TCA cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. They utilize systems such as glutathione to maintain redox homeostasis and promote their own survival. Furthermore, tumor metabolism regulates the immune microenvironment through various pathways: DAMPs released by ferroptosis can promote dendritic cell maturation and activate T cells; while lactate accumulation and IDO1-mediated tryptophan-kynurenine metabolism inhibit T cell function, creating an immunosuppressive environment that collectively impacts anti-tumor immune responses.

(Data source: Jiang J et al. Biomedicines. 2025)
SLC1A5 Targeted therapy
By genetically engineering CAR-NK/T cells (chimeric antigen receptor-modified natural killer cells/T cells) to overexpress molecules such as SLC1A5, the ability of CAR-NK/T cells to recognize tumor cells can be enhanced, while also improving the function, survival ability and long-lasting effect of CAR-NK/T cells in the body, helping them to fight tumor cells more effectively.
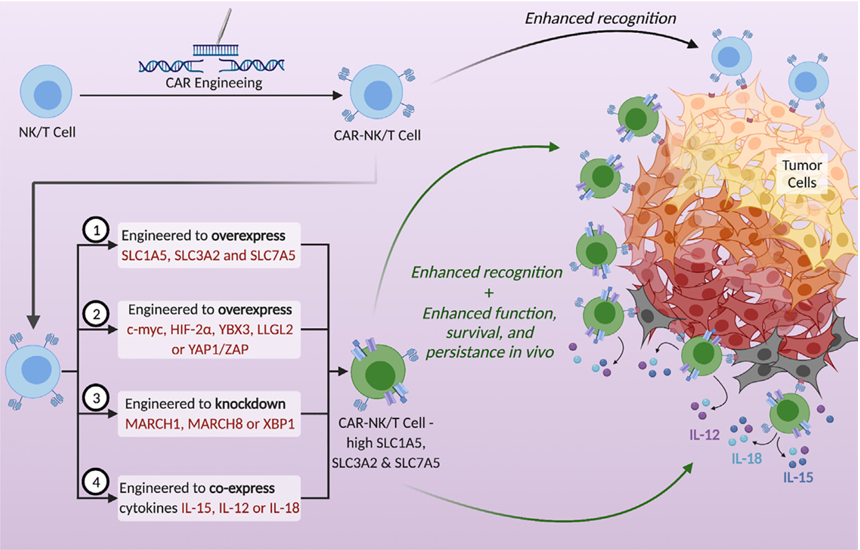
(Data source: Dhar C et al. Front Cell Neurosci. 2023)
Idactamab is a targeted drug ADC developed by AstraZeneca PLC. Its main mechanism of action is as an SLC1A5 inhibitor. The antibody partially targets ASCT2 (SLC1A5), inhibiting its function, thereby blocking the glutamine-dependent metabolic pathway and suppressing tumor growth. The coupled DNA inhibitor can directly damage tumor cell DNA, enhancing the anti- tumor effect. It is intended for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia, advanced malignant solid neoplasms, and colorectal cancer. Phase 1 clinical trials were approved on March 29, 2017, but no progress has been made.
HuB14-VA-PL2202 is a targeted drug developed by ADC Therapeutics SA for SLC1A5 and TopoⅠ. Its main mechanism of action is as an ASCT2 inhibitor and a TOP1 inhibitor. ASCT2 inhibitors: Target the amino acid transporter ASCT2 (SLC1A5) on the surface of tumor cells, inhibiting the metabolic reprogramming and proliferation of tumor cells by blocking the uptake of key nutrients such as glutamine. TOP1 inhibitors: Interfere with DNA replication and repair by releasing topoisomerase I (TOP1) inhibitors, inducing DNA damage and apoptosis in tumor cells. This drug is designed by combining the dual anti -tumor strategies of targeting metabolic pathways (ASCT2) and DNA damage repair (TOP1), and is primarily used to treat solid tumors and hematological malignancies (such as acute myeloid leukemia and lymphoma ). It is currently in the preclinical stage.
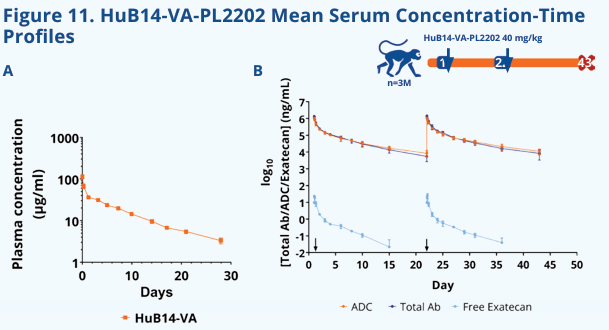
(Date source: Danilo Cucchi et al. Cancer Research. 2025)
