T-cell surface protein tactile, also known as CD96/TACTILE, belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily and is a key inhibitory receptor for immune regulation. It is mainly expressed on the surface of T cells, NK cells and regulatory T cells (Treg). It participates in intercellular signaling through interaction with its ligand CD155 and has research value in pathological processes such as tumor immune escape and autoimmune diseases.
Expression distribution of CD96
CD96 is expressed on normal T cell lines and clones, as well as on some transformed T cells, but is absent from other cultured cell lines tested. It is expressed at low levels on activated B cells.

(Data source: Uniprot)
Function of CD96
The function of CD96 is closely related to the cell types on which it is expressed (primarily NK cells and T cells, especially effector T cells and regulatory T cells (Tregs)) and the location of its ligand, PVR (CD155). PVR is commonly expressed on tumor cells, virus-infected cells, certain antigen-presenting cells, and endothelial cells. Its main functions are as follows:
Mediated adhesion: CD96 binds to PVR on the surface of target cells (such as tumor cells, virus-infected cells) , mediating the physical adhesion between NK cells or T cells and target cells.
Transmitting Inhibitory Signals: After binding to PVR, CD96 primarily transmits inhibitory signals to CD96-expressing immune cells (especially NK cells) , suppressing their cytotoxic activity in the later stages of the immune response. Simultaneously, by competing with the activating receptor CD226 for its ligand PVR, it blocks CD226's co-stimulatory signal and indirectly inhibits CD226's activation function, forming a dual inhibitory mechanism.
Structure of CD96
CD96 is an Ig-like protein encoded by the CD96 gene. It is 585 amino acids long and has a molecular weight of approximately 65 kDa. It is located on the surface of T cells and belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily (IgSF). CD96 is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein with a transmembrane region located between 518 and 540 amino acids. Its extracellular region contains three immunoglobulin-like domains responsible for ligand binding. The intracellular region contains tyrosine phosphorylation sites, which can transmit inhibitory signals. It also contains multiple N-linked glycosylation sites.
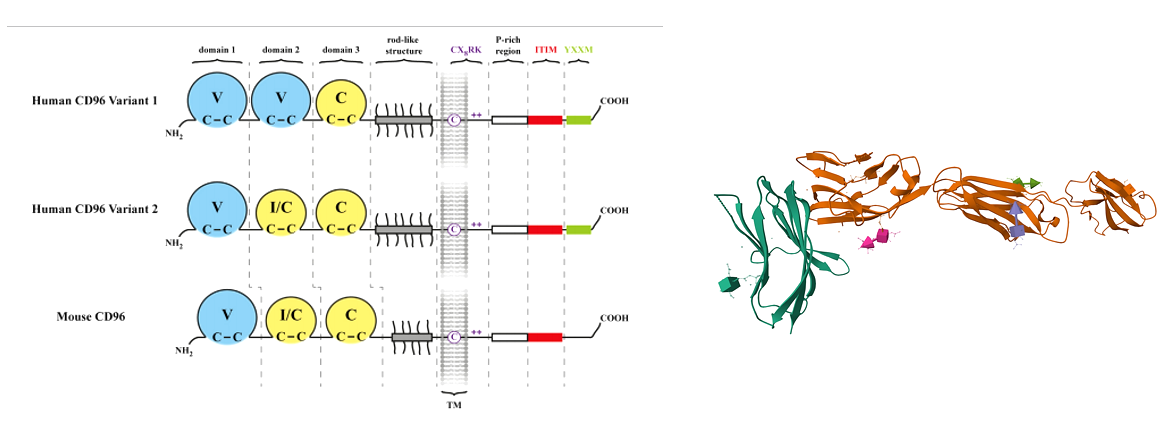
(Data source : Hristo Georgiev, et al. Front Immunol 2018. Right: AlphaFold)
Signaling pathway and regulation of CD96
CD96 is an immunomodulatory receptor primarily expressed on NK cells and T cells. Its signaling pathway is primarily inhibitory. Its core process is as follows: Ligand binding: Binding to CD155 (or CD112) on target cells (such as tumor cells) ; Inhibitory signaling: Phosphorylation of the intracellular ITIM domain recruits SHP-1/SHP-2 phosphatases. Inhibitory effect: Phosphatases negatively regulate downstream activated signaling pathways (such as PI3K/Akt and MAPK), inhibiting cytotoxicity, cytokine secretion, and proliferation. Competitive inhibition: Competing with the activating receptor DNAM-1 for binding to CD155/CD112, synergistically inhibiting the receptor TIGIT, and collectively limiting immune activation.
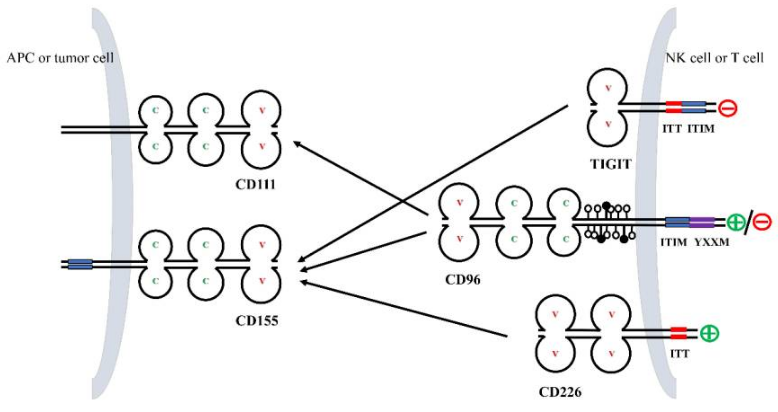
(Data source Feng S, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2023)
CD96 and Disease
CD96 is a key driver of tumor immune escape. Overactivation of CD96 inhibits T/NK cell function, promotes tumor immune escape, and leads to the development of malignancies such as ovarian cancer and melanoma. It also impairs NK cell viral clearance, leading to persistent infection with pathogens such as LCMV. CD96 deficiency can cause the loss of control of effector T cells and exacerbate autoimmune diseases such as encephalomyelitis in animal models. In the treatment of breast cancer, antibodies targeting CD96 can block the CD96-CD155-Src-Stat3-Opa1 signaling axis, inhibiting mitochondrial fatty acid β-oxidation metabolism in tumor cells, reversing chemotherapy resistance and resensitizing tumor cells to chemotherapy. Furthermore, targeting the stemness-maintaining mechanisms of breast cancer stem cells has the potential to improve the efficacy of breast cancer chemotherapy and inhibit tumor recurrence.
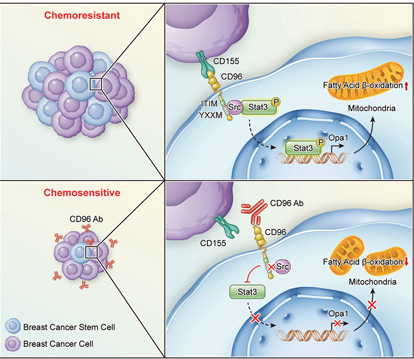
(Data source: Li J , et al. Adv Sci . 2023.)
CD96-targeted therapy
Nelistotug (GSK-6097608) is a humanized IgG1κmonoclonal antibody targeting CD96, developed by GSK Plc. Its primary mechanism of action is as a blocking antibody for CD96, blocking its interaction with CD155. This action relieves immune cell inhibition, restores the tumor-killing activity of T/NK cells, relieves immunosuppression, and promotes the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IFN-γ. It is intended for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer and advanced malignant solid tumors. The first Phase 2 clinical trial in the United States began on January 24, 2019.
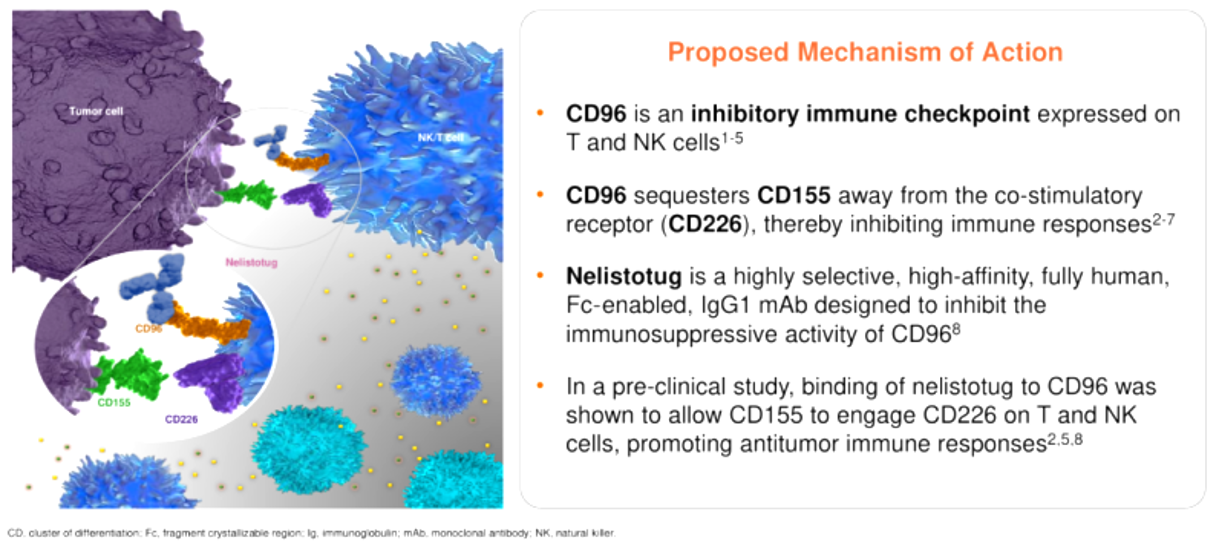
(Data source: Left: GSK Plc official website)
BMS-986442 (AGEN-1777/AGEN1777) is a bispecific antibody developed by Agenus Inc. that targets CD96 and TIGIT. Its primary mechanism of action is similar to that of Nelistotug , as both are CD96 blockers , but it also targets TIGIT. By inhibiting signaling through the co-stimulatory receptor CD226, it weakens the ability of immune cells to kill tumors and enhances the anti-tumor immune response. It is intended for the treatment of advanced cancers and locally advanced malignant solid tumors. The first Phase 2 clinical trial in the United States began on October 4, 2022.
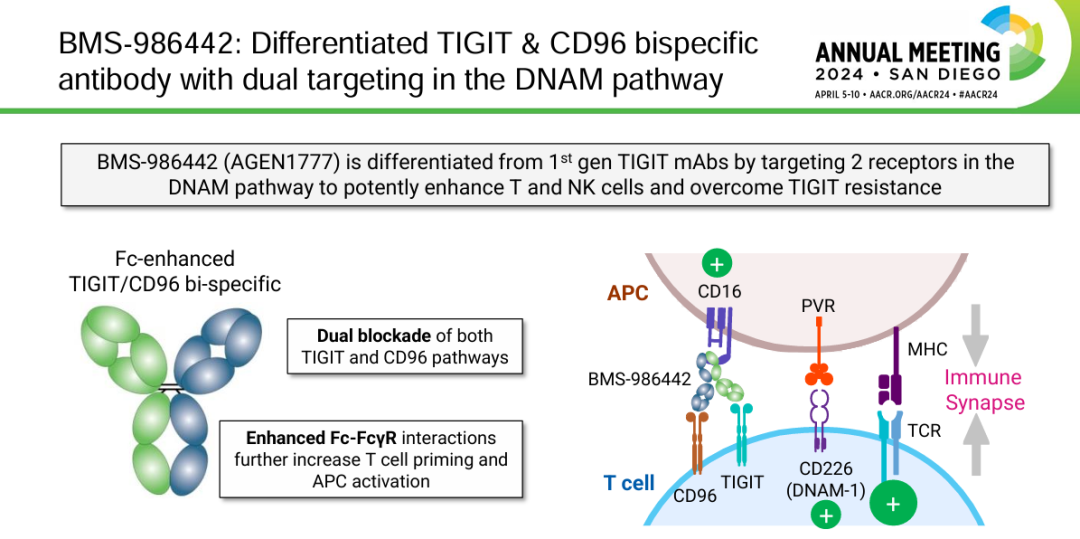
(Data source: ANNUAL MEETING)
Anti-CD96 antibody is a monoclonal antibody targeting CD96 developed by Jiangsu Hengrui Medicine Co., Ltd. and has not yet entered the clinical stage.
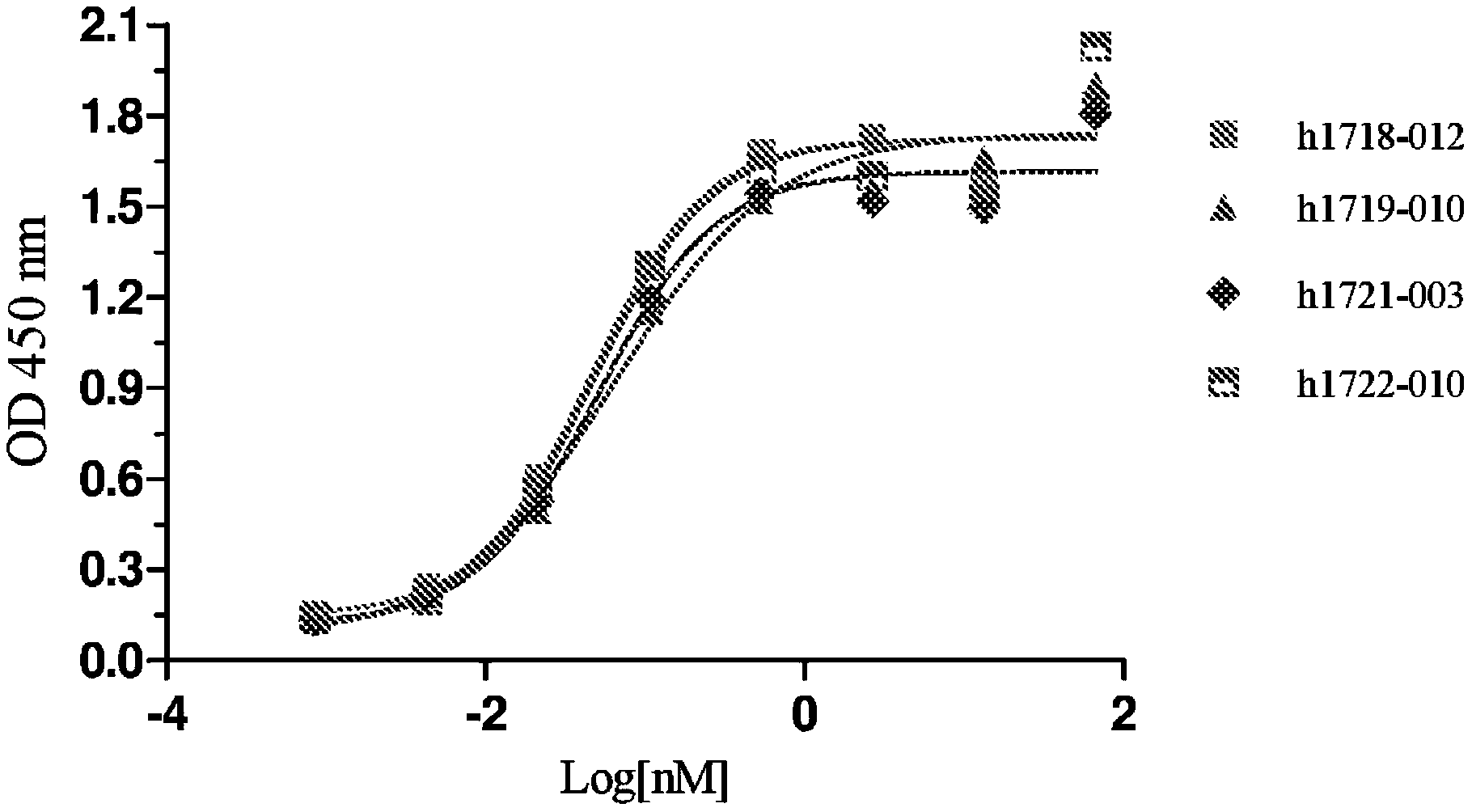
(Data source: China National Intellectual Property Administration)
Anti-CD96 antibody is a monoclonal antibody targeting CD96 developed by Jiangsu Hengrui Pharmaceuticals Co., Ltd and is currently in the preclinical stage.
