Expression distribution of TNFSF14
TNFSF14 is primarily expressed in the spleen and is also found in the brain. Low levels of expression are found in peripheral lymphoid tissues, as well as in the heart, placenta, liver, lung, appendix, and kidney. No expression has been detected in fetal tissues, endocrine glands, or non-hematopoietic tumor cell lines.
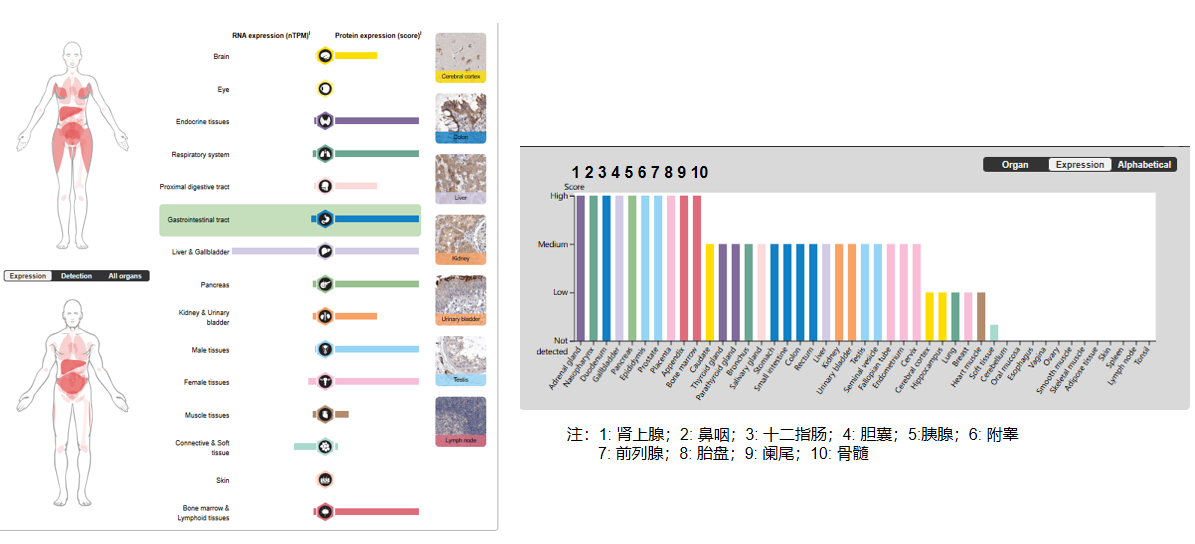
(Data source: Uniprot)
Function of TNFSF14
TNFSF14 acts as a cytokine that binds to TNFRSF3/LTBR. It also regulates its effects by binding to the decoy receptor TNFRSF6B. As a ligand for TNFRSF14/HVEM, upon binding to TNFRSF14/HVEM, it transmits a costimulatory signal to T cells, leading to T cell proliferation and IFN-g production.
Structure of TNFSF14
TNFSF14 is a single-pass type II transmembrane protein with a length of 240 AA and a molecular weight of approximately 26.3 kDa, encoded by the TNFSF14 gene . Its structure consists of three parts: the intracellular region, the transmembrane region, and the extracellular region.
Transmembrane region and protein form: The transmembrane domain is located at AA positions 38–58 and is anchored to the cell membrane. There are two subtypes: membrane-bound (full-length transmembrane protein) and soluble (released after the extracellular region is cleaved by proteases).
Extracellular functional domain: Contains the typical TNF homology domain (THD), composed of approximately 150 amino acids, forming a β-pleated trimer that mediates binding to the receptor.

(Data source : AlphaFold)
TNFSF14 signaling pathway
TNFSF14/LIGHT activates or inhibits downstream signaling pathways by binding to three different receptors (HVEM, LTβR, and DcR3).
HVEM (TNFRSF14)-mediated signaling pathway:
NF-κB pathway: Classical pathway: recruitment of TRAF2/5 → activation of IKK complex → degradation of IκBα → release of NF-κB (p50/p65) nuclear translocation → promotion of T cell and NK cell activation and proliferation → regulation of the expression of pro-inflammatory factors IL-6 and IL-8.
Non-classical pathway: NIK activation → IKKα phosphorylation → p100 processing to p52 → RelB/p52 heterodimer translocation into the nucleus → expression of lymphocyte development-related genes.
MAPK pathway: In some cases, TNFSF14 can activate the phosphorylation of MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) subfamily (such as JNK, p38) through TRAF2, further activating AP-1 transcription factor, thereby regulating the expression of cell apoptosis, proliferation or inflammation-related genes.
LTβR (lymphotoxin βreceptor)-mediated signaling pathway: TNFSF14 competes for binding with membrane-bound lymphotoxin (LTα1β2); LTβR, LTβR→TRAF3 degradation→NIK stabilization→IKKα activation→p100→p52 processing→RelB/p52 nuclear entry.
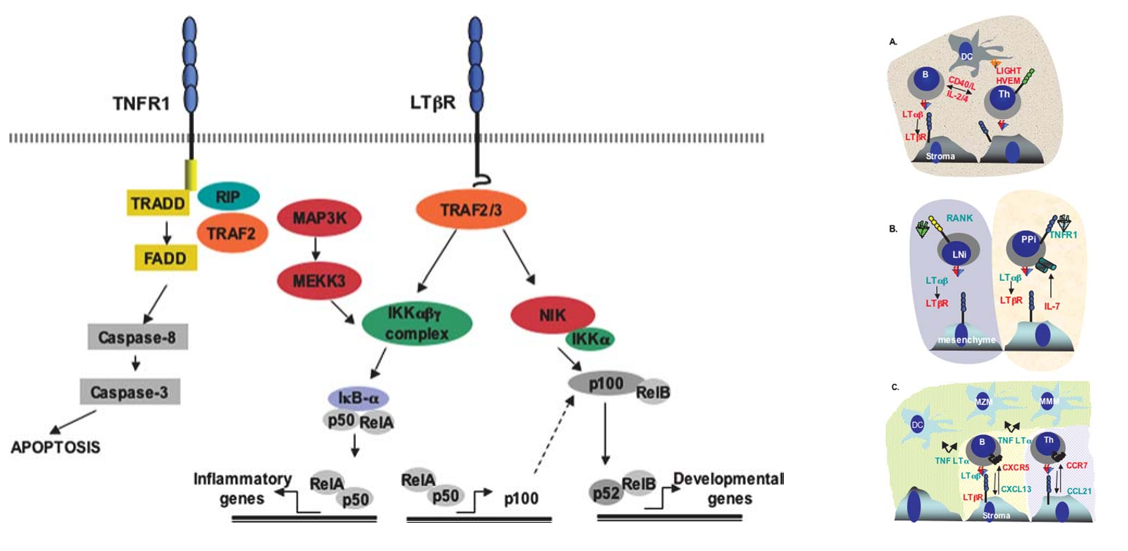
(Data source: Carl F Ware , et al. Annu Rev Immunol . 2005)
TNFSF14 and disease
LIGHT (TNFSF14) promotes the migration, infiltration, and M2 polarization of macrophages in the ventricles and atria. Transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) secreted by LIGHT-stimulated macrophages further promotes the transformation of fibroblasts into myofibroblasts and collagen synthesis, ultimately leading to increased myocardial fibrosis and susceptibility to atrial fibrillation.

(Data source: Yirong Wu , et al. J Transl Med . 2023)
Gastric cancer: TNFSF14 is highly expressed in cancer tissues, especially in patients with advanced stage (stage III/IV), promoting tumor immune escape and invasion.
Rheumatoid arthritis: Low TNFSF14 expression leads to abnormal T cell activation, promoting the release of inflammatory factors (such as IFN-γ) and exacerbating joint damage. The upstream regulatory factor miR-3074-5p participates in the pathogenesis of RA by targeting and inhibiting TNFSF14 expression .
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and intestinal barrier damage: TNFSF14 maintains the function of intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs) through the HVEM-CD160 pathway. Its abnormal function can destroy the intestinal mucosal barrier and promote the development of IBD.
Targeted therapy of TNFSF14
To break through the limitations of the tumor microenvironment, cell vectors, viral vectors, and protein vectors/viral vectors can be selected to efficiently deliver LIGHT, causing "immune reprogramming" of the tumor microenvironment, activating anti-tumor immunity, inducing the formation of lymph node-like structures in the tumor, recruiting and activating T cells, and enhancing local immune responses.
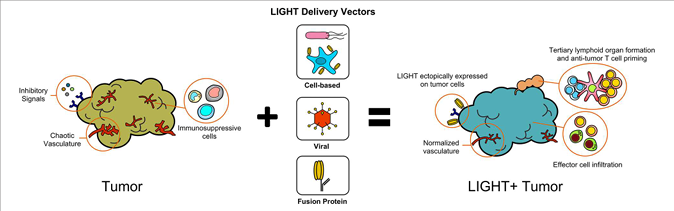
(Data source: Joseph G Skeate , et al. Front Immunol . 2020)
Quisovalimab, a humanized monoclonal antibody targeting LIGHT, was developed by Kyowa Kirin Co., Ltd. Its primary mechanism of action is as a LIGHT inhibitor, suppressing excessive inflammation by blocking LIGHT signaling. It is suitable for the treatment of acute lung injury and respiratory distress syndrome in autoimmune diseases, metabolic disorders, and tumors with high LIGHT expression. A Phase 2 clinical trial in the United States began on June 23, 2016 and has since been terminated .
CBS-001 , a monoclonal antibody targeting light, is being developed by Capella Bioscience Ltd. Its primary mechanism of action is to act as a light stimulator, enhancing light-mediated immune activation and reshaping the tumor or infection microenvironment for the treatment of pulmonary fibrosis. A Phase 1 clinical trial in the United States began on April 14, 2022.
GB24, developed by Sinovac Biotech, is a bispecific antibody targeting both VEGI and LIGHT. Unlike Quisovalimab, it is not only a LIGHT inhibitor but also a VEGI inhibitor, thus enhancing its ability to synergistically regulate angiogenesis and the immune microenvironment, potentially enabling its use in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. It is currently in the preclinical stage.
TNFSF14-related CAR-T therapy: Modified Pbbz-LV CAR-T cells secrete light. Light binds to LTβR on the surface of tumor and stromal cells, prompting them to secrete chemokines (such as CCL19, CCL21, CXCL9, CXCL10, and CXCL11), which in turn recruit immune cells to form tertiary lymphoid structures (TLS) and promote immune infiltration. Furthermore, the HVEM receptor on the surface of these CAR-T cells can bind to autocrine or paracrine light, enhancing its anti-tumor activity and cytotoxicity.
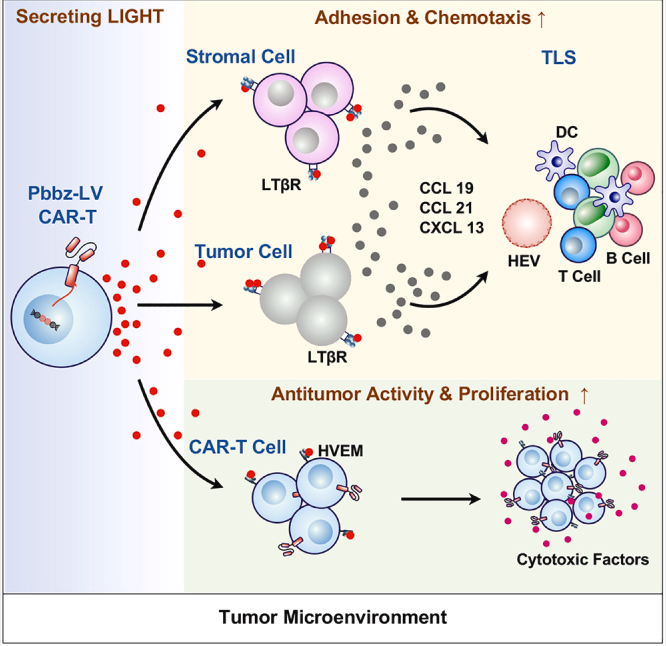
(Data source: Na Zhang, et al. Mol Ther. 2023)
