CDH17 is a cadherin protein belonging to a subclass of the 7D-cadherin family. Its primary function is cell-cell adhesion, which may be involved in tumorigenesis. The adhesion mechanism of CDH17 differs from that of typical cadherins. While classic cadherins require complexing with α-and β-catenins, CDH17 maintains its adhesive function without interacting with other cytoplasmic components. CDH17 may serve as a potential biomarker for liver and gastric cancers.
Expression distribution of CDH17
CDH17 is primarily expressed in glandular epithelial cells, endocrine cells, and undifferentiated cells. It is barely expressed in hepatocytes, esophageal epithelial cells, and gastric mucosa in healthy individuals. In tumor tissues, CDH17 is overexpressed in gastric, pancreatic, liver, esophageal, bile duct, and colorectal cancers.

(Data source: uniprot)
Structure of CDH17
CDH17 is a transmembrane protein composed of an extracellular region consisting of seven cadherin domains, a short cytoplasmic domain (only 20 amino acids), and a transmembrane region. This structure differs from that of classic cadherins, which have five cadherin domains in their extracellular region and a cytoplasmic region of approximately 150-160 amino acids. CDH17 contains an RGD site, which could serve as a novel ligand for integrin binding.

(Data source: Bartolomé RA, et al. J Biol Chem. 2014)
The role of CDH17 in cancer
CDH17 binds to integrin α2β1 on adjacent tumor cells through its RGD motif, which leads to enhanced integrin activation, adhesion, proliferation, invasion, tumorigenesis, and metastasis.

(Data source: Marshall JF. Clin Cancer Res. 2018)
Targeted therapy for CDH17
CDH17 is considered a potential target for cancer treatment. Therapeutic strategies targeting CDH17 may inhibit tumor cell proliferation and metastasis by blocking its interaction with integrins, thus having therapeutic potential.
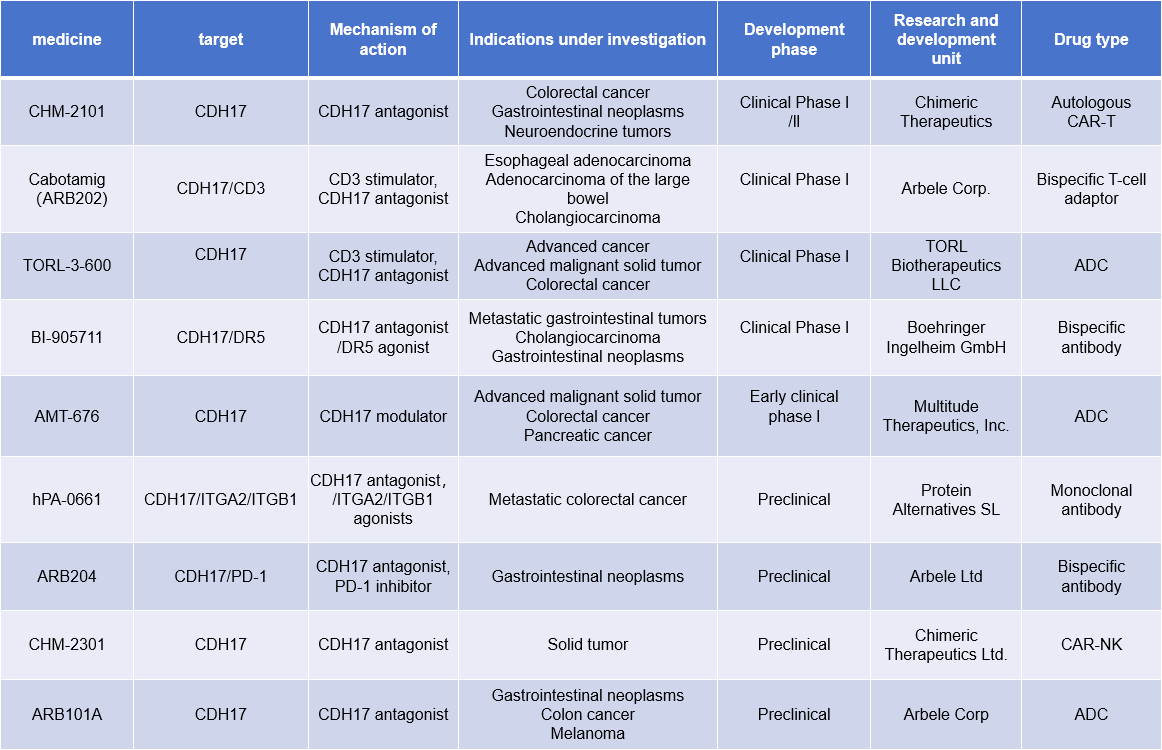
(Data source: New Drug Intelligence Database)
CHM-2101 is a third-generation CDH17-targeted CAR-T therapy developed by Chimeric Therapeutics. The clinical program for CHM 2101 builds on preclinical studies published in March 2022 in the renowned scientific journal “Nature Cancer” by Xianxin Hua, MD, a leading immunotherapy scientist at the Abramson Cancer Center of the University of Pennsylvania, and his team. These studies demonstrated that CHM 2101 eradicated established tumors in seven cancer models while being nontoxic to normal tissue. Currently in Phase I/II clinical development, CHM-2101 is being evaluated for the treatment of colorectal cancer, gastrointestinal tumors, neuroendocrine tumors, and other diseases.
Cabotamig ( ARB202 ) is a humanized bispecific T cell engager antibody developed by Arbele Corp using TriAx technology. TriAx antibodies feature two novel core structures designed to achieve low antigenicity, stability, and optimal biodistribution and pharmacokinetics. TriAx antibodies combine mechanisms such as T/NK cell cytotoxicity redirection, immune checkpoint inhibition, phagocytosis, and enhancement of adaptive immune responses. ARB202 is primarily designed for the treatment of gastrointestinal cancers and is currently in Phase 1 clinical development.

(Data source: Arbele Corp official website)
