The glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor (GLP1R) is an important member of the G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) family. It specifically interacts with GLP-1, a key hormone that plays an integral role in regulating blood glucose levels, lipid metabolism, and several other critical biological functions. GLP1R plays a crucial role in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and is a therapeutic target for obesity and metabolic disorders.
GLP1R expression distribution
GLP1R is mainly present on the surface of various cell types in the human body, such as cardiomyocytes, exocrine gland cells, pancreatic endocrine cells, melanocytes, inhibitory neurons, and mammary cells.
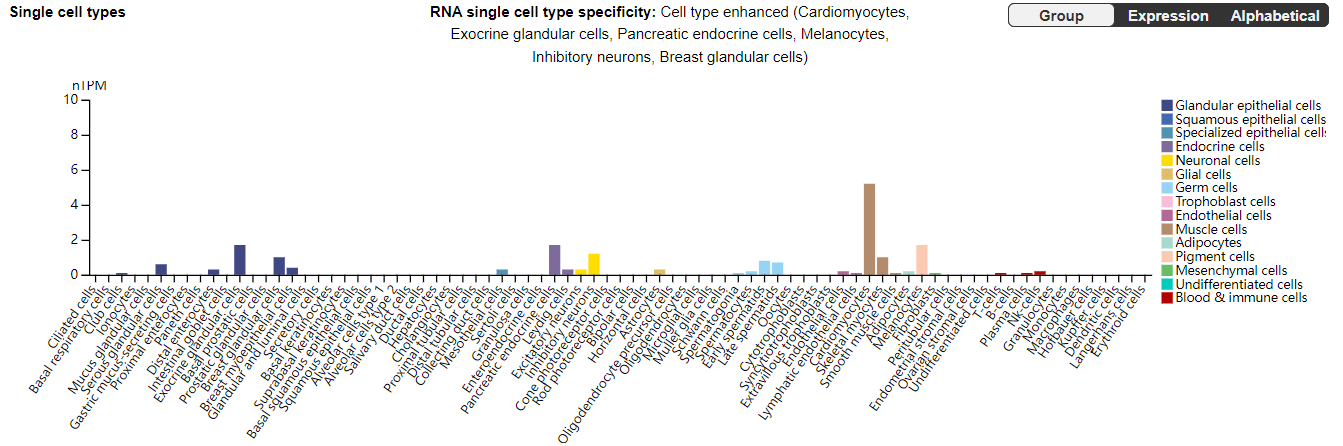
(Data source: uniprot)
Structure of GLP1R
GLP1R is a seven-transmembrane protein composed of 463 amino acids. GLP1R consists of a large amino-terminal extracellular domain (ECD) and a transmembrane domain (TMD) with a typical seven-transmembrane helix structure (TM1-TM7). The N-terminal ECD domain of the GLP1R protein forms a three-layered α-β-βα fold stabilized by three pairs of cysteine disulfide bonds. The N-terminal ECD binds to the C-terminal helix of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) to initiate peptide recognition, while the TMD is responsible for binding to the N-terminal portion of the peptide to activate the receptor and trigger its downstream signaling cascade.

(Data source: Jazayeri A, et al. Nature)
GLP1R signaling pathway and regulation:
GLP1R primarily signals through the Gαs/cAMP pathway; evidence suggests that GLP1R couples to Gαq and other G proteins. Upon activation, GLP1R undergoes C-terminal phosphorylation, further recruiting β-arrestin, leading to receptor internalization and desensitization. The Gαs/cAMP pathway directly contributes to glucose-induced insulin granule secretion. Upon activation by full agonists such as GLP-1, GLP1R couples to Gαs, activating adenylate cyclase (AC) and leading to cAMP accumulation. This cAMP accumulation further activates protein kinase A (PKA) and the cAMP exchange protein Epac-2, which directly activates cAMP. These kinases trigger the closure of K ATP and K V channels, leading to membrane depolarization, opening voltage-dependent calcium channels (VDCCs), and initiating Ca2+ influx. In addition to the Gαs/cAMP pathway, GLP1R can also couple to other G protein isoforms, such as Gαi, Gαq, Gαo, and Gα11, resulting in complex downstream signaling pathways. Regulation of the GLP1R signaling pathway is crucial for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Through these pathways, GLP1R agonists can lower blood glucose, reduce weight, and potentially provide cardiovascular protection.

(Data source: Wan W, et al. Molecules. 2023)
GLP1R targeted therapy:
Currently, there are a large number of drugs targeting GLP1R, including 15 GLP1R agonist drugs on the market globally, including 6 recombinant peptides, 7 synthetic peptides, and 2 hormones.

(Data source: New Drug Intelligence Database)
There are also many drugs targeting GLP1R in clinical research, including monoclonal antibodies, bispecific antibodies, antibody fusion proteins and other drugs targeting GLP1R.
Glutazumab (GMA102) is a humanized anti-GLP1R monoclonal antibody carrying a GLP-1 fragment, developed by Hongyun Huaning Biopharmaceuticals for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and is currently undergoing Phase 3 clinical trials.
GMA106 is a bispecific antibody targeting GIPR and GLP1R, reducing appetite and body fat accumulation by modulating these two pathways. With its extended half-life, GMA106 can achieve a better dosing schedule (weekly or monthly) and higher patient compliance. In preclinical studies, GMA106 has demonstrated excellent efficacy in reducing weight, particularly body fat content, and may become a highly effective treatment for obesity, NASH, and T2DM.
ZX2021 is an Fc-fused GLP1R/GIPR/GCGR triple agonist developed by Zhongxin Pharmaceutical and is in Phase 1 clinical trials for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. In preclinical studies, ZX2021 has demonstrated excellent weight loss and glucose-lowering effects, outperforming existing single-target drugs.
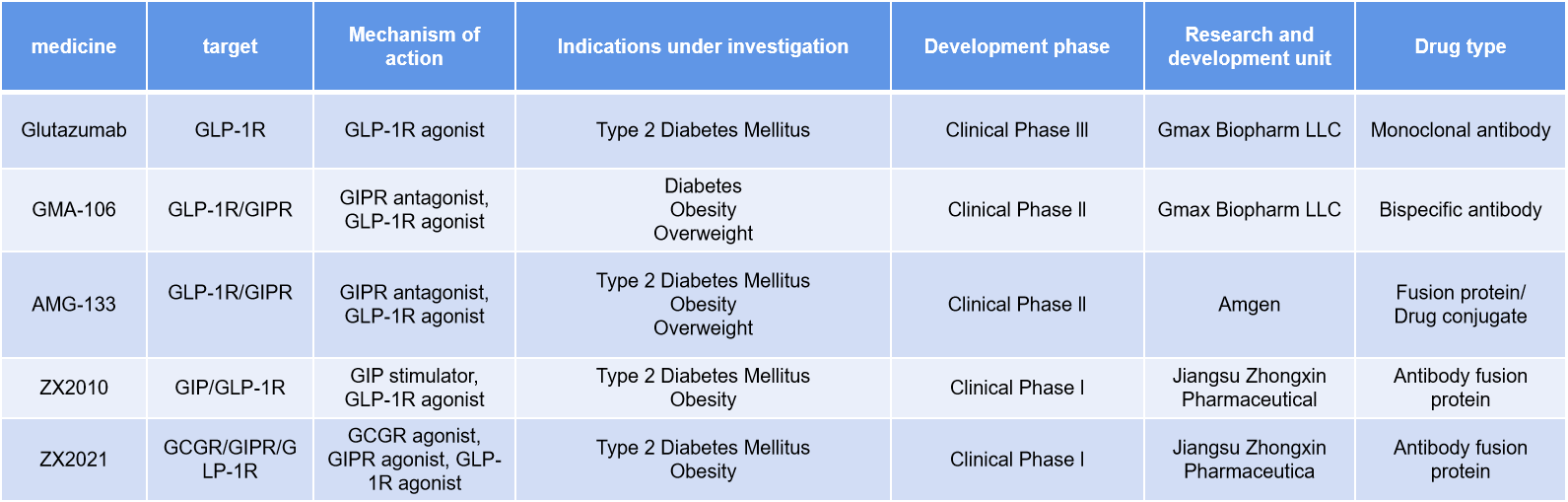
(Data source: New Drug Intelligence Database)
