The tyrosine protein kinase transmembrane receptor ROR2 belongs to the receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) superfamily. ROR2 is expressed during embryonic development and participates in Wnt signaling, activating multiple tumor-promoting pathways and implicated in embryonic development and cancer progression.
Expression distribution of ROR2
ROR2 is mainly expressed in adipocytes, Hofbart cells, and cardiomyocytes, and is also expressed in small amounts in macrophages, Kupffer cells, dendritic cells, Langerhans cells, and erythroid cells.
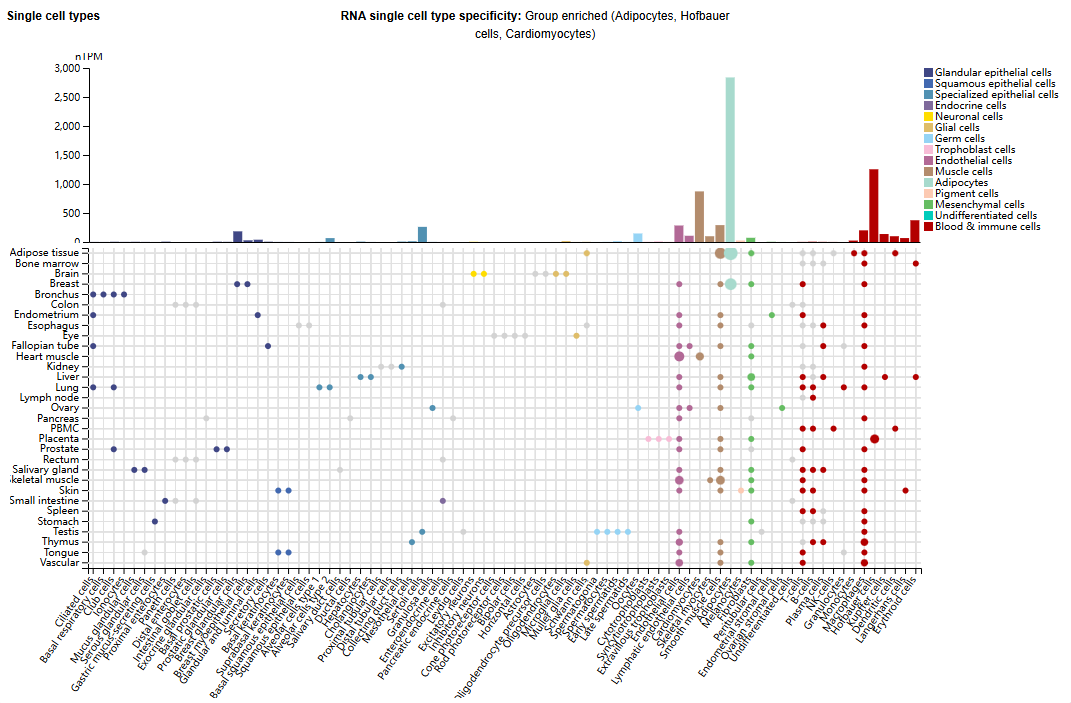
(Data source: Uniprot)
The structure of ROR2 and its receptor
ROR2 is a type I transmembrane protein. As a member of the RTK family, the structure of ROR2 consists of three main parts: extracellular, transmembrane, and intracellular regions. The extracellular region of ROR2 is divided into several domains: an immunoglobulin (Ig)-like domain, a cysteine-rich domain (CRD), and a Kringle domain. ROR2 has a CRD in the extracellular region that is characterized by 10 conserved cysteines and some additional conserved amino acids. CRDs are mainly composed of α-helices and serve as binding sites for Wnt ligands. The Ig-like domain consists of approximately 100 amino acid residues, including a conserved disulfide bond, and is thought to mediate protein-protein interactions and also modify the functions of the CRD and Kringle domain. The Kringle domain is a trisulfide-linked domain that has been reported to act as a recognition module to bind to other proteins and promote cell migration.
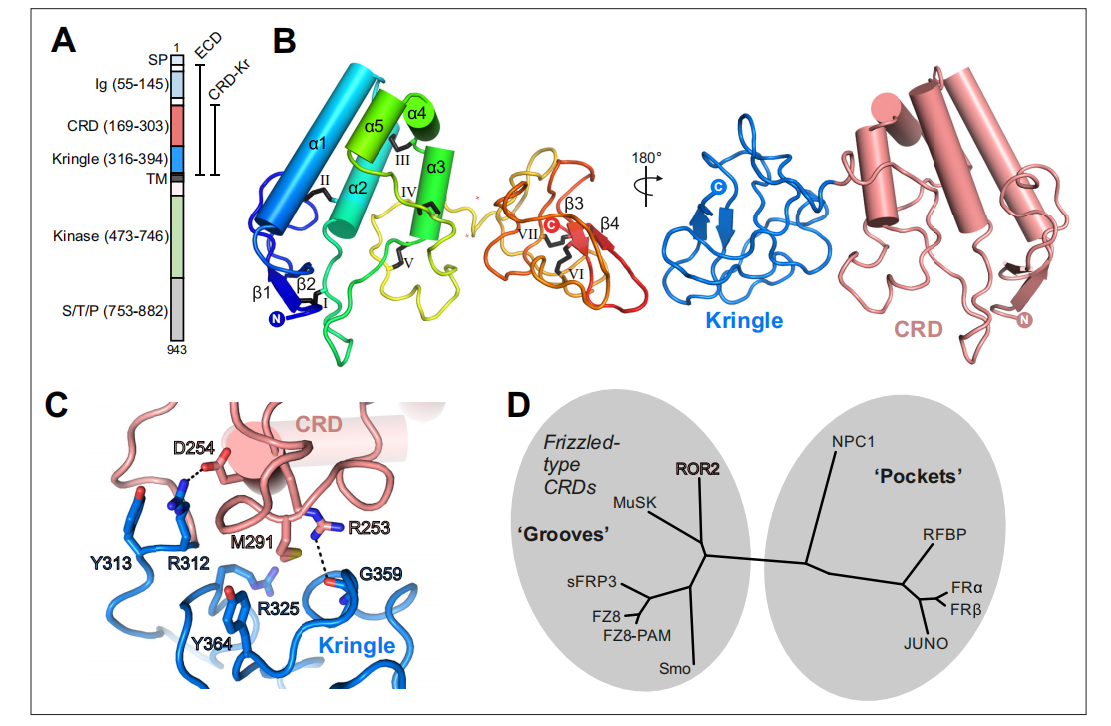
(Data source: Griffiths SC, et al. Elife. 2024)
Signaling pathway and regulation of ROR2
ROR2 regulates the non-canonical WNT pathway. Interaction between the Wnt ligand Fzd and ROR2 leads to phosphorylation of ROR2 in the cytoplasm by GSK3β or CKIε. Once activated, ROR2 recruits Dvl2, which promotes both JNK activation of the PCP pathway and PKC activation, both of which are associated with migration and invasion. Furthermore, Dvl2 activation by ROR2 can inhibit the β-catenin-dependent canonical Wnt signaling pathway by activating CAMKII in the Wnt calcium pathway, thereby targeting β-catenin for degradation.

(Data source: Castro MV, et al. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2022)
The role of ROR2 in cancer
ROR2 has a dual role in cancer, acting both as a tumor suppressor and a promoter of tumor growth.
Tumor promotion
The expression of ROR2 is associated with tumor development. When ROR2 is overexpressed, it promotes cell proliferation, migration, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) by activating multiple signaling pathways (such as Rho family GTPases, MAPK/JNK and MAPK/p38), and increases treatment resistance.
Tumor suppressor effect
When ROR2 expression is reduced, it exerts a tumor suppressive effect by inhibiting related signaling pathways, suppressing proliferation, promoting apoptosis, inhibiting EMT, and increasing chemotherapy sensitivity.

(Data source: Castro MV, et al. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2022)
Targeted therapy for ROR2
Due to the role of ROR2 receptors in the progression of various types of cancer, their restricted expression in adult tissues, and their overexpression in tumor cells, they are considered potential targets for new therapies. The localization of ROR2 on the cell surface makes it an excellent target for monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). As a result, many antibodies targeting ROR2 are in late-stage clinical trials for different tumor types, such as CLL, metastatic breast cancer, and B-cell lymphocytic malignancies.
Ozurift amab vedotin (BA-3021), a ROR2-targeting antibody-drug conjugate developed by BioAtla, is a conditionally activated ADC that exploits the acidic nature of the tumor microenvironment (TME). BA3021 consists of an engineered antibody specifically targeting ROR2, conjugated to the cytotoxic payload MMAE via a cleavable linker, precisely responsive to the pH characteristics of the TME. Under normal physiological conditions, BA3021 has minimal binding affinity for its target antigen; however, in the acidic TME (pH 5.3-6.7), its binding affinity is significantly enhanced. This property enables BA3021 to specifically target tumor tissues while effectively minimizing off-target toxicity to normal tissues.
On June 2, 2025, BioAtla presented Phase 2 clinical trial data from ozuriftamab vedotin (Oz-V) at a conference. The data showed significant antitumor activity in HPV-associated oral pharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (HPV+ OPSCC) at a 1.8 mg/kg Q2W dosing schedule. The FDA granted ozuriftamab vedotin Fast Track designation for the treatment of recurrent or metastatic SCCHN. BA3021 is being evaluated as a monotherapy and in combination with a PD-1 inhibitor (nivolumab) in patients with ROR2 -expressing melanoma, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), and ovarian cancer ( NCT03504488 ).
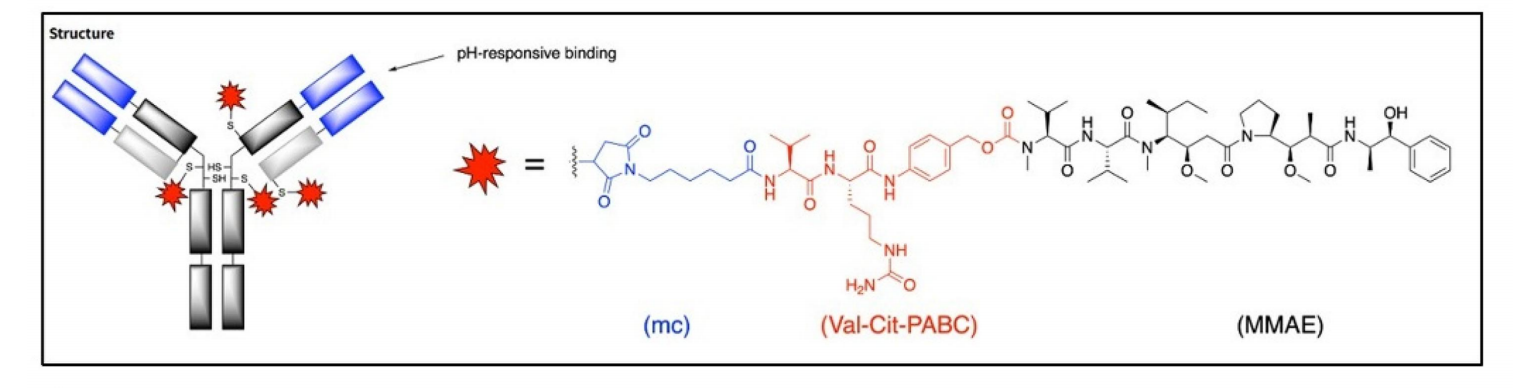
(Data source: Chang HW, et al. MAbs. 2025)
TB-Bs1 is a bispecific T cell engager targeting ROR2 for the treatment of high-grade serous ovarian cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, and anaplastic large cell lymphoma. This product is being developed by Traverse Biotech in collaboration with Genmab S/A and is currently in preclinical development.
