Leucine-rich G protein-coupled receptor 5 (LGR5), acting as a receptor for R-vertebral proteins (RSPO1, RSPO2, RSPO3, or RSPO4), enhances the classical Wnt signaling pathway and functions as a stem cell marker in intestinal epithelium and hair follicles. LGR5 participates in cancer development and progression through multiple pathways, including the WNT/β-catenin signaling pathway. LGR5 plays a role in various cancers, including colorectal cancer, brain cancer, gastric cancer, and ovarian cancer, by promoting cancer cell migration, invasion, metastasis, and angiogenesis.
LGR5 expression distribution
LGR5 is mainly expressed in myocytes, trophoblast cells, glial cells, luminal cells, stem cells, and supporting cells of secretory glands. Under pathological conditions, especially in cancer, the expression pattern of LGR5 is significantly altered. In malignant tumors such as colorectal cancer, liver cancer, and ovarian cancer, LGR5 is overexpressed.

(Data source: uniprot)
LGR5 Structure
LGR5 is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). The human LGR5 gene consists of 144,810 bases and is located on chromosome 12, specifically at 12q22-q23. LGR5 includes an N-terminal extracellular domain (17 leucine-rich repeat (LRR) domains), three intracellular loops (ICL1-ICL3), a transmembrane region of seven hydrophobic α-helical transmembrane domains responsible for signal transduction, and three extracellular loops (ECL1-ECL3), as well as a C-terminal domain. LGR5, together with the 17 LRR domains, forms a curved solenoid structure and does not interact with small molecule ligands, hormones, or neurotransmitters as typical GPCRs do.
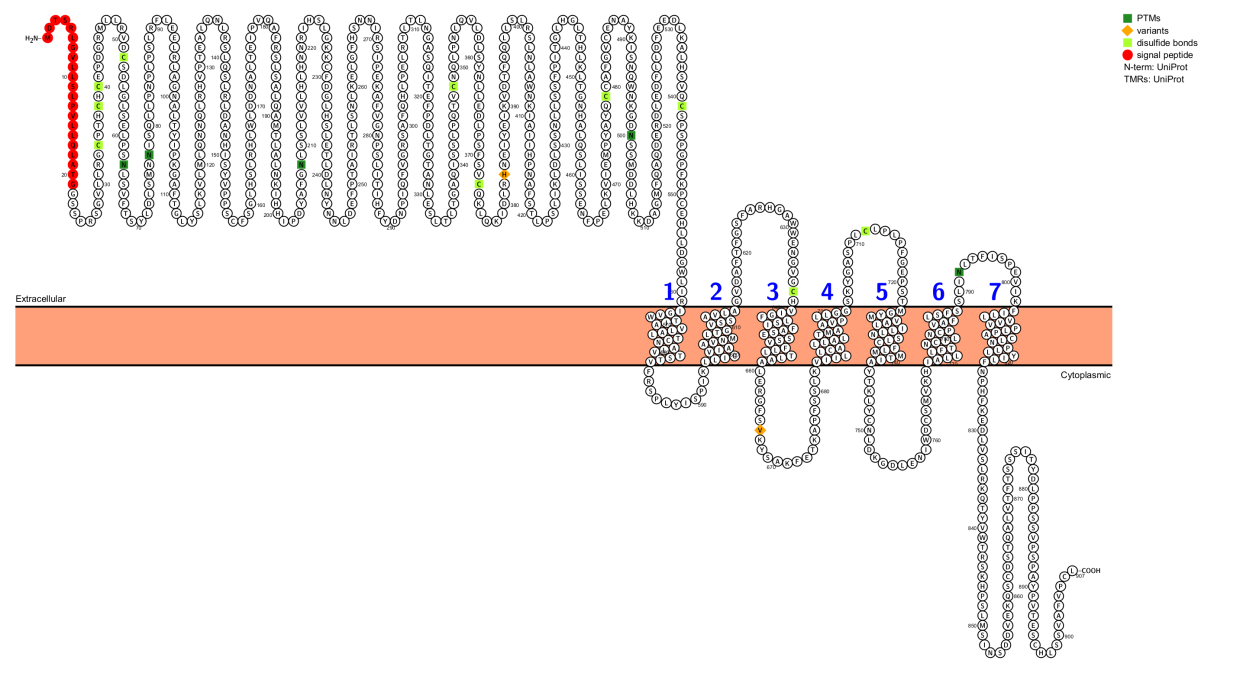
(Data source: uniprot)
LGR5 Functions
LGR5 is an important stem cell marker involved in the maintenance and renewal of stem cells in various tissues, including the intestine, stomach, hair follicles, and ovary. It is a target of the WNT/β-catenin signaling pathway, crucial for regulating stem cell proliferation and tissue homeostasis. Unlike classic G protein-coupled receptors, this receptor does not activate heterotrimeric G proteins to transduce signals. During post-embryonic development, it participates in the development and/or maintenance of adult intestinal stem cells.
When LGR5 binds to its ligand RSPO, it forms a complex with RNF43/ZNRF3. This interaction isolates the E3 ubiquitin ligase, preventing its degradation of Wnt receptors. An increase in the number of stable Wnt receptors (Frizzled and LRP5/6) on the cell membrane significantly enhances the cell's sensitivity to Wnt signaling in the microenvironment. This enhanced Wnt signaling ultimately leads to the accumulation of β-catenin in the nucleus, activating the transcription of a series of target genes (including LGR5 itself), thereby driving stem cell self-renewal, proliferation, and inhibiting differentiation. This pathway is crucial for maintaining the homeostasis of intestinal crypt stem cells, and its aberrant activation is a driving force behind many cancers. In the absence of LGR5 (or in the absence of WNT signaling), RNF43/ZNRF3 degrades Fzd, thereby downregulating WNT signaling.
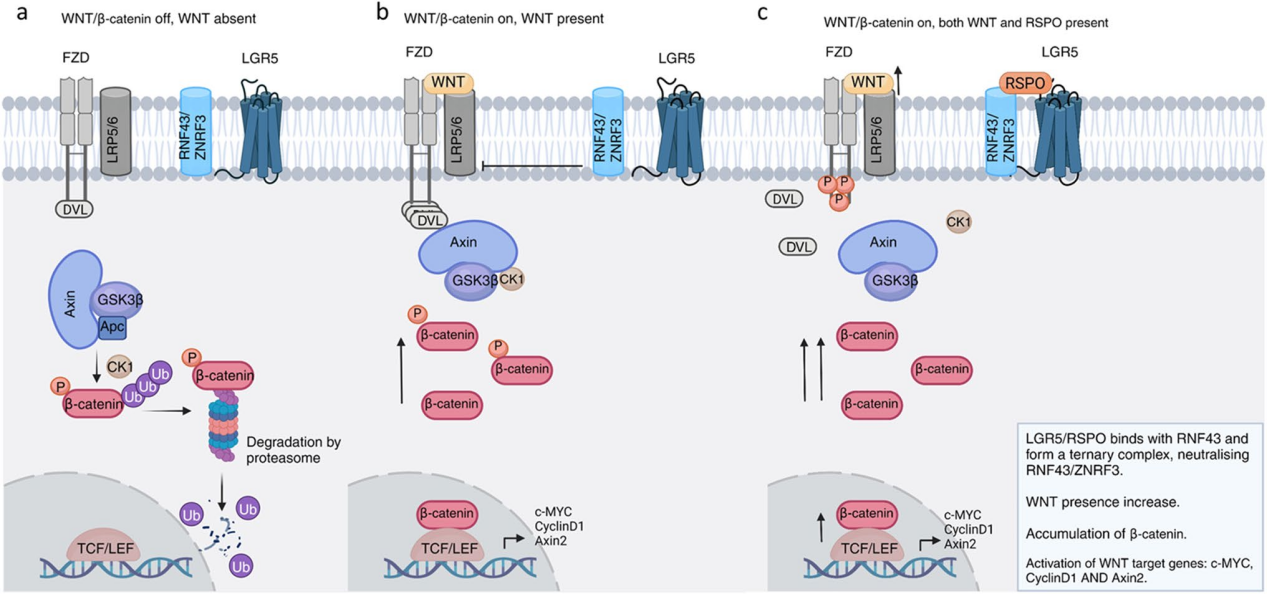
(Data source: Wang W, et al. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2025)
LGR5-targeted therapy
LGR5 is highly expressed in a variety of solid tumors, especially in cancer stem cell subpopulations, making it a very popular therapeutic target. There are many bispecific antibodies, ADCs, and CAR-T cell immunotherapies targeting LGR5 in clinical trials.
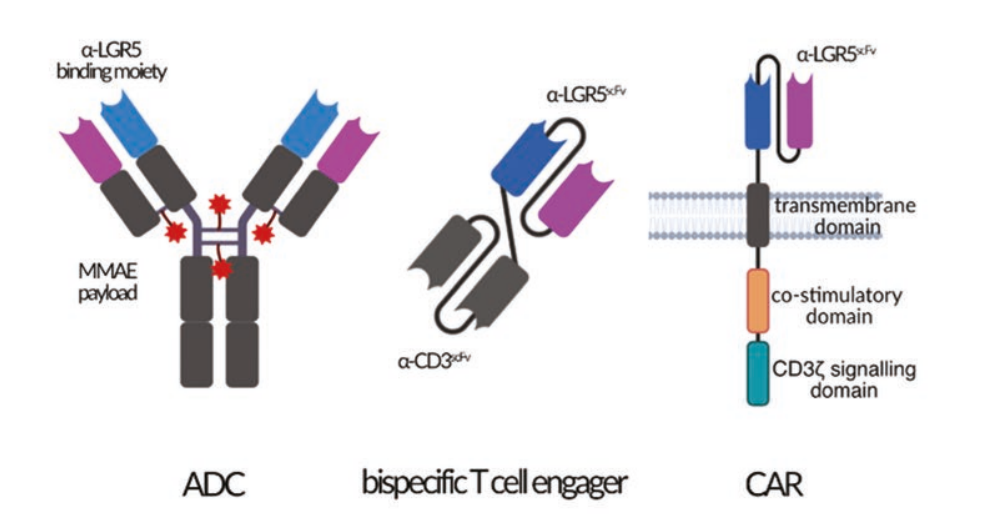
(Data source: Mueller N, et al. Immunother Adv. 2025)
Petosemtamab (MCLA-158) is a bispecific antibody that targets EGFR and LGR5, a leucine-rich repeat sequence. Petosemtamab has three independent mechanisms of action: inhibition of EGFR-dependent signaling, LGR5 binding leading to EGFR internalization and degradation in cancer cells, and enhanced antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity and antibody-dependent phagocytic activity. Petosemtamab is being developed as a first-line treatment for patients with PD-L1+ recurrent/metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (r/m HNSCC). The LiGeR-HN1 trial is a phase III, open-label, randomized controlled trial comparing the efficacy and safety of petosemtamab plus pembrolizumab versus pembrolizumab alone.
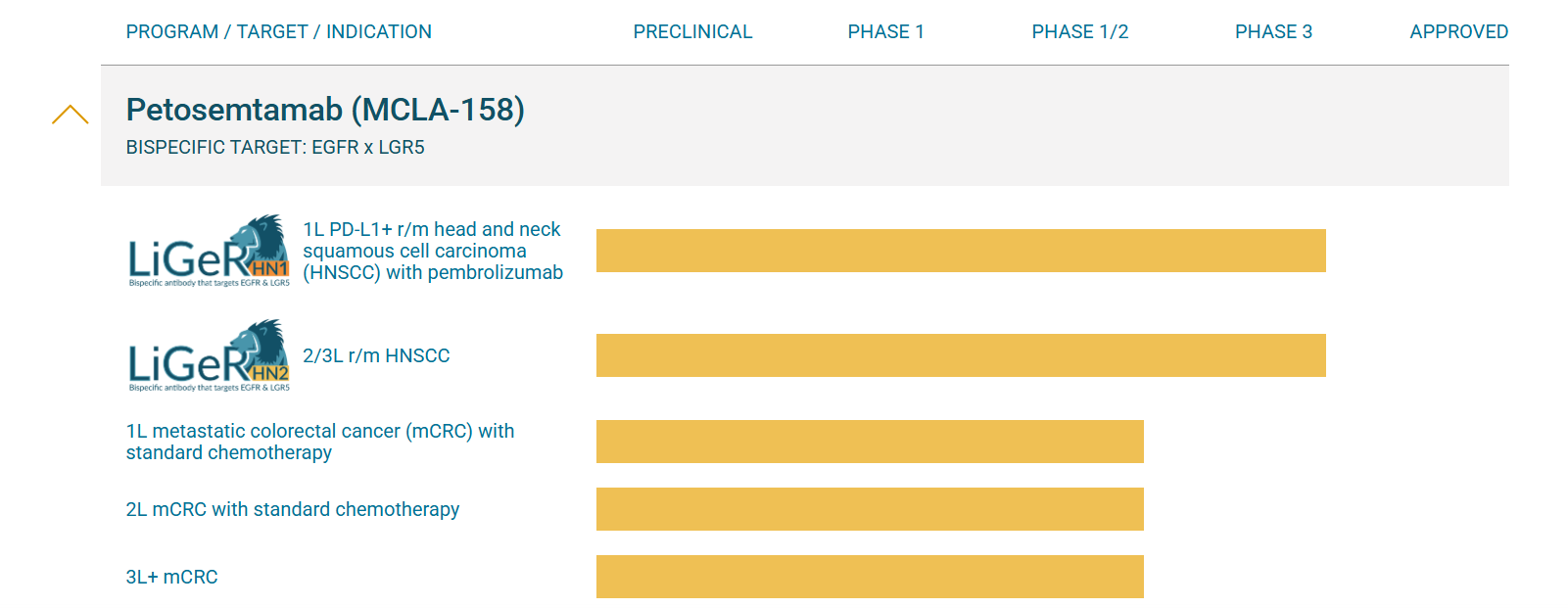
(Data source: Merus NV official website)
CNA-3103 is a CAR-T cell therapy targeting LGR5 developed by Carina for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer, colorectal cancer, and hematologic malignancies. Carina's preclinical studies of CNA3103 showed promising efficacy, with complete tumor reversal and no recurrence after a single dose. CNA3103 also demonstrated enhanced tumor entry and prolonged survival, thereby promoting the rejection of new tumors.
8E11-CPT2 is an antibody-drug conjugate targeting LGR5 with significant antitumor efficacy. Combination therapy of 8E11-CPT2 with CTX has shown additive or synergistic activity in gastrointestinal cancer cells, regardless of mutation status, and significantly reduced tumor burden and prolonged survival in patients with recurrent acute gastrointestinal (RAS). Combined administration of CTX with an LGR5 ADC may feasiblely expand its clinical efficacy in patients with mCRC harboring oncogenic mutations in the EGFR signaling pathway (such as KRAS or PIK3CA).

(Data source: High PC, et al. Cell Rep Med. 2025)
